Respiratory System
100 likes | 207 Vues
The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide. Learn about the parts involved, from the nose and mouth to the lungs, and how breathing is essential for life.

Respiratory System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Respiratory System The body system that brings oxygeninto the body and removes carbon dioxidefrom the body
Respiration • The absorption of oxygen (inhale) • Release of carbon dioxide and water (exhale) • The bloodstream delivers the oxygen to the cells and picks up the “garbage” • Carbon dioxide, which is oxygen that has been used by the cells and water. • How can you prove there is water in the exhale?
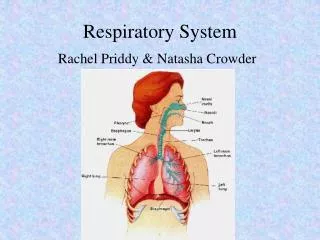
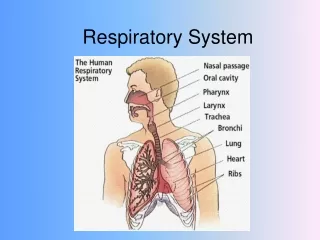
Parts Air enters the body through the nose and mouth. Then, air passes into the pharynx Pharynx – an intersection of tubes (larynx, esophagus, and back of nasal passage) Nostrils – Have hair to capture air particles Nasal Cavities – Open area behind nostrils separated by the septum (means to separate)
Parts cont. Eustachian tube – runs from inner ear to throat so excess fluid can drain out of the ears If it can’t – it causes earaches/infections and you will need “tubes” put in ear drum so fluid can drain out. Throat infections, like strep, can travel up the eustachian tubes and affect the ears
Parts Cont. Turbinates – air circulates around these to : sticky, so they pick up smaller particles Warm the air They have olfactory nerve endings to give us smell
Parts cont. Sinuses – small cavities in skull that hold liquid that drips into the nasal passage to: 1) warm the air 2) humidify it Uvula – covers the back of the nasal passage so food/liquids/vomit don’t come out nose as you swallow/throw-up Tonsils – soft tissue at side of throat to capture bacteria
Parts cont. After the pharynx, air passes into the larynx. Larynx – 2 folds of tissue covering the top of the windpipe that vibrate for sound. When tightened = voice raises When loosened = voice lowers
Parts cont. From the larynx, air enters the windpipe, or trachea Trachea – tube that carries air – has rings of cartilage around it Cilia – small hair lined in the trachea. They sweep the air and move tiny particles to stick to mucus.
Parts cont. The trachea divides into two tubes called bronchi. Bronchi – 2 tubes that branch off the trachea into the lungs. Bronchitis – an infection of these tubes Bronchioles – tubes inside the lungs that get tinier until they end at the alveoli Alveoli – tiny air sacs where the gases are exchanged with the bloodstream
Parts cont. The movement of air into and out of the lungs is caused by the movement of the diaphragm. Diaphragm – a sheet of muscle in the chest that allows breathing Inhale = work Exhale = relax When the diaphragm and the muscles between the ribs contract, air enters the lungs.