Types of Reliability and Validity
220 likes | 1.04k Vues
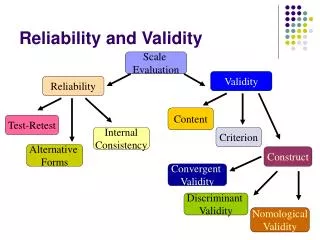
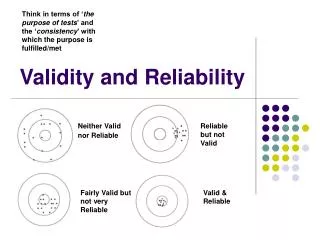
Types of Reliability and Validity. Research Methods (cont’d). Types of Reliability. There are four types of reliability measures. For a test/experiment to be deemed ‘reliable,’ it must yield consistent results no matter the circumstances . Four types: Inter-rater Test-retest

Types of Reliability and Validity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Types of Reliability and Validity Research Methods (cont’d)
Types of Reliability • There are four types of reliability measures. For a test/experiment to be deemed ‘reliable,’ it must yield consistent results no matter the circumstances. • Four types: • Inter-rater • Test-retest • Parallel-forms • Internal consistency
Types of Reliability (cont’d) • Inter-rater reliability= the test/experiment yields similar results no matter who is giving the test. • This eliminates observer bias. • Test-retest reliability= the test/experiment yields similar results across time. • Factors that can influence test variation: mood, disruptions, time of day. • An unreliable test will vary greatly in results depending on these factors.
Types of Reliability (cont’d) • Internal consistency reliability= the test/experiment will yield similar results, even though different questions are asked. • Questions are different, but material is similar in construct. • Example: The following two questions test the same knowledge, although phrased differently. • Which social science looks at past cultures and societies? • Past cultures and societies are the predominant focus of which social science?
Types of Reliability (cont’d) • Parallel forms reliability= used to determine the best versionof a test/experiment. • Different people take different versions of a test at the same time. • These two versions are done in parallel, to determine which is best. • Example: two field tests are given to students at two different schools on the same day. Whichever test yields more consistent results becomes the nationwide test.
Types of Validity • A test that has validity accurately measures what it is supposed to. • There are 4 main types of validity that are important to sociological research: • Construct validity • Content validity • Conclusion validity • Face validity
Types of Validity • Construct validity= determines the quality of an instrument, test or experiment. • Does it measure what it is designed to measure? • Content validity= measures what it is supposed to measure AND includes an adequate sample. • Does the measurement include different groups or does it focus on the knowledge/characteristics of one specific group?
Types of Validity (cont’d) • Conclusion validity= a relationship between two variables can be determined, either positive or negative. • Face validity= appears to be valid on the surface. This should not be the sole factor in determining validity!!! • It can, however, be a good springboard for experimental design– does your experiment seem like it will work?