Ancient India
420 likes | 662 Vues
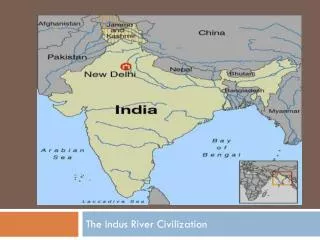
Ancient India. Chapter 7. Geography and Indian Life Lesson 1. Physical Geography of India Subcontinent : a large landmass similar to, but smaller than, a continent. Mountains and Waterways Himalayans : mountains in the northeast. Hindu Kush: mountains in the northwest.

Ancient India
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ancient India Chapter 7
Geography and Indian LifeLesson 1 Physical Geography of India • Subcontinent: a large landmass similar to, but smaller than, a continent. Mountains and Waterways • Himalayans: mountains in the northeast. • Hindu Kush: mountains in the northwest. • Indus River Valley: Ganges River and Indus River. • Saraswati dried up.
Climate • Monsoons: seasonal winds • Winter: little moisture from the north. • Northern mountains block cold winds • Summer: Heavy rains from the southwest. • Water picked up from the Indian Ocean
Cities in the Indus Valley • We know about these cities because of writing that was discovered on tablets. However, no one can decipher them yet. Early Inhabitants • Agriculture led to cotton, which ledto fabric • Copper, bronze tools Great Cities • Mohenjo-Daro, Harappa (35,000 people) • Indus valley culture named after Harappa • Planned cities: cities built by design Dealing with Problems • Human waste: sewage systems
Harappan Culture • Seals contain info that can’t be read • 500 pictographs Religion • Huge bath for cleansing • Animals “bulls” important A Widespread and Prosperous Culture • 2 times the size of Texas • Wealth came from agriculture / trade • Measurement: used weights Challenges to the Harrapan Life • Earthquakes • Flooding People left
The Origins of HinduismLesson 2 Aryans Move into India • Nomads that were forced from homeland fought with advanced weapons The Indo-European Migrations • Possibly forced from home due to natural disaster, plague, and / or invasion
The Aryan Invasions • 1500 B.C. crossed into India • Historians believe the Harappan civilization could have been destroyed by a natural disaster sucha s a flood or earthquake
Changes to Indian Life • The Aryans practiced a mysterious religion • Religion spread and India developed a complex culture
The Caste System • Aryan society was organized into classes, which developed into the caste system • Born into class • Must marry within caste, can only have friends within caste. • Untouchables – did jobs that no one wanted (sweeping dead bodies)
Brahmana: priests, teachers, scholars Ksatriya: rulers, nobles, warriors Vaisya: bankers, merchants, farmers Sudra: artisans, laborers Untouchables: outside the system and below it. They did jobs no one else wanted, such as being sweepers and disposers of dead bodies.
Aryan Beliefs and Brahmanism • Early religion of the Aryan’s that later evolved into Hinduism • Ceremonies that lasted for days and months • Worshipped many gods, kept records, and sacrificed animals
Hinduism: The Religion of India • The Bhagavad Gita is the most important text for the religion and philosophy developed in Ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and Supreme Being who takes many forms.
Many Gods • Hinduism is polytheism • Considered all gods to be part of one universal god • They had gods for the creator, protector, and destroyer
Who do Hindus worship? – the major gods of the Hindu Pantheon Brahma, the creator god
Vishnu, the protector god Incarnates as ten avatars (descents) including: • Rama (featured in the Ramayana • Krishna (featured in the Mahabharata) (Each shown with his consort, Sita and Radha, respectively)
Shiva, god of constructive destruction(the transformer) Appears as Shiva Nataraj,lord of the dance of creation… and with his wife, Parvati, and son Ganesha(the elephant headed remover of obstacles)
What about the goddesses?Devi – the feminine divine Saraswati, goddess of wisdom, consort ofBrahma
Durga, protectress • Kali, destroyer of demons • Plus about 330 million other deities
All these deities are but Manifest forms (attributes and functions) of the impersonal Brahman
Hinduism Continued… Many Lives • Karma: the belief that the deeds (actions) of a person affect what he or she will be in the next life. • Reincarnation: the belief that each person has many lives • Animals have a supreme life force • Many Hindus don’t eat meat as a result.
Many Paths to God • Faithfully carry out duties in life • Some believe by following their own path they can connect with their supreme God • Meditation / yoga
Buddhism and India’s Golden AgeLesson 3 Build on What You Know • Ahimsa = nonviolence The Rise of Buddhism • Based on the teachingsof Siddhartha Gautama • Prince who gave up wealth and powerto understand the meaning of life
The Buddha’s Life and Teachings • Priestpredicted that Siddhartha Gautama be selfless, wandering holy man • At age 29, saw sickness, old age, poverty, and death for the first time in his life. • 6 years of fasting / meditation
Four Noble Truths 1. People sufferbecause their minds are not at ease 2. That condition comes from wanting what one does not have 3. People can stop suffering by not wanting 4. People can stop wanting by following the eightfold path
Eightfold Path • They believe that the Eightfold Path can lead to nirvana
Buddhism Changes • Dharma is collected teachings • After Buddha died, Buddhism divided into many branches
Asoka the Buddhist King • Lived a bloody life but tried to rule peacefully • Carved policies on peacefulness on rocks and pillars • Let people of other religions worship freely (tolerance)
Changes to Hinduism • Language difference drove people away • Many people turn to Buddhism, which meant many people left Hinduism • Poets wrote poems in a language that people could understand, which led to people coming back to Hinduism
The Golden Age of Guptas The Gupta Empire • Chandra Gupta II took India into the Golden Age
Art and Literature • Architecture and art flourished under Chandra Gupta II’s reign • Religious subjects were the basis for art • Kalidasa wrote love stories (most famous was about forgotten women and the royal family)
Mathematics, Science, and Metallurgy • Indian scholars invented the numeral system, symbol for zero, and the decimal system • Ayurvedic improves health by diet, exercise and other methods • Calculate the value of pi and discovered the amount of days in a year • Pillar was built of iron (didn’t rust)
Trade Spread Indian Culture • Traders and missionaries spread Indian culture in many parts of Asia • Gupta profited from foreign trade
The Legacy of IndiaLesson 4 India’s Religious Legacy • Yoga / meditation is very popular and shows that religious traditions are still alive
India’s Religious Legacy (cont.) Hinduism and Buddhism Today • 4 / 5 are Hindus • Asia, Europe, and parts of the west practice Buddhism (Hinduism = worldwide)
Hindu and Buddhist Influences • Gandhi uses ahimisa (nonviolence) - Martin Luther King Jr. was influenced by him • Millions practice meditation
India’s Artistic Legacy • Art worldwide • Many Asian nations use plays from India • Indian art and architecture have helped shape other cultures • Religious art
The Legacy of Indian Mathematics • Numerals originated in India • Decimal also developed in India • Discover zero • Arab traders brought numerals; hence, Arabic numerals