Understanding Cell Structure: The Building Blocks of Life
180 likes | 309 Vues
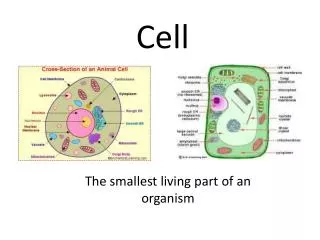
Cells are the smallest living units of organisms, comprising specialized parts called organelles that perform essential functions. Tissues consist of groups of cells working collectively. Organs are made up of different tissues that collaborate to execute specific tasks, while organ systems encompass groups of organs working together. Key components include the cell membrane that regulates substance movement, the nucleus that directs cell activities, mitochondria for energy release, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Understanding these structures reveals the complexity and functionality of life.

Understanding Cell Structure: The Building Blocks of Life
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell The smallest living part of an organism
Organelle A specialized part of a cell having some specific function for the cell
Tissue A group of cells that work together to perform a certain function for an organism
Organ A group of different tissues that work together to perform a certain function in an organism
Organ System A group of organs that work together to perform a certain function in an organism
Turgor Pressure The pressure exerted on a cell membrane or cell wall
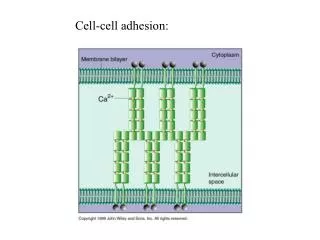
Cell Membrane A soft, flexible structure that surrounds a cell and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Cell Wall A rigid, outer covering of a plant cell
Nucleus The structure in a cell that controls everything the cell does
Mitochondrion The structure in a cell that release energy from the nutrients in food
Cytoplasm A jelly-like liquid that fills most of the cell
Chloroplast A tiny green structure that contains chlorophyll, found in the leaf of the plant and needed for energy transformations involving photosynthesis
Vacuole Spaces in the cell that store water and nutrients until the cell needs them or store wastes until the cell can get rid out them
Organism A living object
Heredity The transfer of genetic material from parents to offspring
Chromosomes Thread-like bodies that carry genetic material
Genes The basic unit of heredity
Homeostasis The tendency of a system to maintain internal stability