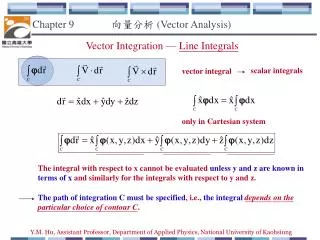
Chapter 13 – Vector Functions
160 likes | 554 Vues
Chapter 13 – Vector Functions. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration. Objectives: Determine how to calculate velocity and acceleration. Determine the motion of an object using the Tangent and Normal vectors. Position Vector.

Chapter 13 – Vector Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 13 – Vector Functions 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration • Objectives: • Determine how to calculate velocity and acceleration. • Determine the motion of an object using the Tangent and Normal vectors. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Position Vector • Suppose a particle moves through space so that its position vector at time t is r(t). • Notice from the figure that, for small values of h, the vector approximates the direction of the particle moving along the curve r(t). • Its magnitude measures the size of the displacement vector per unit time. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Velocity Vector • The vector 1 gives the average velocity over a time interval of length h and its limit is the velocity vector v(t) at time t : • The velocity vector is also the tangent vector and points in the direction of the tangent line. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Speed • The speed of the particle at time t is the magnitude of the velocity vector, that is, |v(t)|. • For one dimensional motion, the acceleration of the particle is defined as the derivative of the velocity: a(t) = v’(t) = r”(t) 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Visualization • Velocity and Acceleration Vectors 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Example 1 • Find the velocity, acceleration, and speed of a particle with the given position function. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Newton’s Second Law of Motion • If the force that acts on a particle is known, then the acceleration can be found from Newton’s Second Law of Motion. • The vector version of this law states that if, any any time t, a force F(t) acts on an object of mass m producing an acceleration a(t), then F(t) = ma(t) 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Example 2 – pg. 871 # 28 • A batter hits a baseball 3 ft above the ground toward the center field fence, which is 10 ft high and 400 ft from home plate. The ball leaves the bat with speed 115 ft/s at an angle of 50o above the horizontal. Is it a home run? (Does the ball clear the fence?) 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration • When we study the motion of a particle, it is often useful to resolve the acceleration into two components: • Tangential (in the direction of the tangent) • Normal (in the direction of the normal) 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration • Writing aTand aN for the tangential and normal components of acceleration, we have a = aTT+ aNN where aT =v’ and aN =v2 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration • We will need to have aT =v’ and aN =v2 in terms of r, r’, and r”. To obtain these formulas below, we start with v · a. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Example 3 – pg. 871 # 38 • Find the tangential and normal components of the acceleration vector. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Kepler’s Laws Note: Read pages 844 – 846. • A planet revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit with the sun at one focus. • The line joining the sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. • The square of the period of revolution of a planet is proportional to the cube of the length of the major axis of orbit. 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
More Examples The video examples below are from section 13.4 in your textbook. Please watch them on your own time for extra instruction. Each video is about 2 minutes in length. • Example 3 • Example 5 • Example 6 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
Demonstrations Feel free to explore these demonstrations below. • Kinematics of a Moving Point • Ballistic Trajectories 13.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration