Atomic Structure
250 likes | 376 Vues
This guide explores the fundamental structure of atoms, which comprise protons, neutrons, and electrons. It discusses how the atomic number determines the number of protons, and thus the identity of an element along with its corresponding electrons. The atomic mass, calculated from protons and neutrons, provides insights into isotopes. Additionally, Bohr's model illustrates the arrangement of electrons in orbitals and how groups and periods on the periodic table reveal similarities among elements. Learn about valence electrons and the classification of elements as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.

Atomic Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
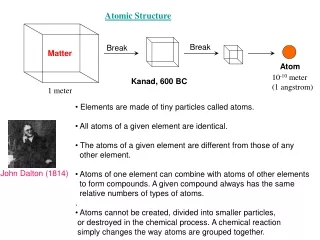
Elements All elements are composed of only one type of atom. In these atoms are three subatomic particles: Protons Neutrons Electrons
Elements -Protons have a positive charge (+) -Neutrons have no charge (neutral) -Electrons Have a negative charge (-)
Most of the mass of an atom is found in the nucleus which contains the neutrons and protons.
Atomic number • Atomic number tells you how many protons that elements has. • If the number of protons changes, the element changes.
Atomic number • Since the atom of an element is neutral, then the atomic number also tells you how many electrons you have. Atomic #=# of protons =# of electrons
Atomic Mass • Atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. • # of protons + #of neutrons = atomic mass
Neutrons • To find out how many neutrons and element has: • Round atomic mass to nearest whole number • Subtract atomic number from atomic mass to get number of neutrons Atomic Mass – Atomic Number = # of neutrons
Example • Na (sodium) • Atomic mass is 22.989 • Atomic mass rounded 23 • Atomic number is 11 Atomic Mass – Atomic Number = # of neutrons • 23-11= 12 • Na has 12 neutrons.
Try these!!! Co (Cobalt) Ag (Silver) Atomic massis 107.868 Atomic mass rounded 108 Atomic number 47 108-47 = 61. • Atomic mass is 58.933 • Atomic mass rounded 59 • Atomic number 27 • 59-27= 32
Bohr’s model • Is a physical drawing that shows where all the subatomic particles are located in a particular atom of an element. • The Bohr’s model is similar to our very own solar system.
Bohr’s Model • Protons and neutron are always found in the nucleus of the atom of an element. • Electrons are around the atom in an area called the electron cloud. • In this electron cloud are orbitals where electrons move around the nucleus of the atom.
Bohr’s Model • Each orbital can only hold a certain amount of electrons: • 1st orbital- 2 electrons • 2nd orbital- 8 electrons • 3rd orbital- 8 electrons • 4th orbital- 18 electrons
The elements found in a group have similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons.
The horizontal rows on the periodic table are called a period. Periods tell you how many orbitals will be on your drawing. • Ex. Na (sodium) is in Period 3, it will have 3 orbitals in its Bohr’s Model.
The vertical columns on the periodic table are called groups. Groups tell you how many valence electrons the element has. • Ex. Na (sodium) is in Group 1 so it has 1 valence electron.
Valence electrons are the electrons that occupy the last orbital of an element. • Orbitals are also called energy levels.
Boron (B) 5 p+ 6 n
Al 13 p+ 14 n
Lewis-Dot Structure • The amount of dots you draw for a Lewis Structure (LS for short) is equal to the # of Valence Electrons in an Atom
Valence Electrons • The # of Valence e- an atom has is dictated by the Group that the Element is in • Groups are the Vertical Columns on the Periodic Table!!! It’s So Simple!!!!
Isotopes are atoms of a given element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers.
Ex. Oxygen-16; has 8 neutrons Oxygen-17; has 9 neutrons Oxygen-18; has 10 neutrons These are all still oxygen atoms.
Elements on the periodic table are classified as one of the following: • Metals • Nonmetals • Metalloids