ECHO
250 likes | 522 Vues
ECHO. A System Monitoring and Management Tool. Yitao Duan and Dawey Huang. Challenge. How can we manage all these machines?. Goal. Aimed at networked system management Better tools for Discovering system states Enhancing system availability Monitoring network and system statistics

ECHO
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ECHO A System Monitoring and Management Tool Yitao Duan and Dawey Huang
Challenge • How can we manage all these machines?
Goal • Aimed at networked system management • Better tools for • Discovering system states • Enhancing system availability • Monitoring network and system statistics • Error detection and correction • Fault tolerance for specific network applications (such as web server)
Overview • Distributed agents gathering information • Centralized Control Unit (CCU) monitors and analyzes data. Takes control action if needed • Script language for automatic decision making • Web browser user interface
EchoMe Daemon SNMP Tool
Centralized Control Unit • Information collection • Machine information • Network information • Information analysis • Individual Machine analysis • Collaborative network analysis • Action • System modification • Network routing
Information Collection • Two approaches investigated • EchoMe Daemons running on hosts and reporting system information to server • SNMP to discover router connectivity and states • Daemon mostly for collecting local information. Much more detailed • SNMP for network connectivity
EchoMe Daemon • Automatically discover a node (node reporting stage) • EchoMe Daemon start up as machine boot • Send up OS type/machine info to CCU • Register a session in CCU • CCU sends to node a monitor program base on node’s OS/Machine type and execute it on the node. • Monitor program send up information packet periodically to CCU.
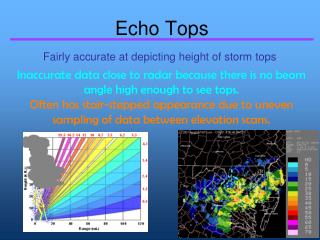
Router Connectivity Discovery by SNMP • Routers implemented SNMP • Program can run on any host within Millennium • Given a router (can get from local host’s gateway information), query its ipRouteTable • Traverse all its neighboring routers, performing the same query • Recursion stops at specified distance
System Information • Number and speed of the CPUs • Total physical and swap memory Installed • System Clock • Uptime • Kernel Version • Percent CPU user, nice, system and idle • One, five and fifteen minute load averages • Number of running processes and total number of processes • Amount of free, shared, buffered, cached and swap memory
Network Information • Network Interfaces • /proc/dev or CTL_NET/AF_LINK • SNMP: interface.ifTable • ARP cache – direct neighbors • /proc/arp or RTF_LLINFO • SNMP: ip.ipNetToMediaTable • Route Table • /proc/route or NET_RT_DUMP • SNMP: ip.ipRouteTable
Information Analysis • CCU a relational database • Front end, parsing engine • Individual Node Analysis • Collaborative Analysis
Parsing Engine • IPACKET is in standard XML format • IPACKET use incremental update, new packet specifies differences from previous packet. • Parsing Engine parses the IPACKET into objects and does the insertion to iface accordingly. • <ID ??> <DATATYPE> DATA </DATATYPE></ID>
IFACE Tables • The client node register an unique nodeid in iface_node_table • It starts a session for reporting information to CCU • Each time, client node reports information by sending up an information packet. (ipacket) • CCU process this packet, create an unique statement id from iface_index_table and parse information into each iface_?DATA_table.
Individual Node Analysis • Clean up iface_?data_table by transferring and categorizing data into each nodes’ own data table. • A background process runs on CCU. • Examples: • Network statistic overtime table • Network route change reporting • Network usage of nodes. (packets, tcp/udp connection counts) • Node’s system state overtime table • Node’s configuration change table
Collaborative Analysis • Group up specify information in the iface_?data_tables and ninfo_?data_tables to generate special tables for user viewing/analysis. • Examples • Network connectivity graph • Network graph between two node or route • Network snapshot table • All nodes’ current network statistic table • All nodes’ current state table
Interface to View Analysis • Web interface • Viewable under web browser • Web session • Display analysis • Take action input from user • Java Servlet + JSP • Security control • Data Objects map with tables in collaborative analysis
Action • Daemon capable of receiving and executing binary programs from CCU • Command module issues command in response to certain events • Add pseudo interface to a host • Reroute a host • Initialize new program • Etc.
Security • OpenSSL encryption • EchoMe Daemon Run as nobody • System Modification Program needs to do suexec (ROOT PASSWORD requires)
Transcripts for SNMP Router Discovery …… Iterating neighbors of 169.229.51.202 .... IP address: 169.229.51.161(A9E533A1) IP address: 169.229.51.233(A9E533E9) IP address: 169.229.51.165(A9E533A5) IP address: 169.229.51.167(A9E533A7) IP address: 169.229.51.168(A9E533A8) IP address: 169.229.50.33(A9E53221) IP address: 169.229.50.129(A9E53281) IP address: 169.229.51.166(A9E533A6) IP address: 169.229.51.169(A9E533A9) IP address: 169.229.51.234(A9E533EA) In getIPRouteTable. nHops = 8 Setting target to 169.229.51.234 ……
169.229.51.198 169.229.51.233 169.229.51.167 169.229.51.169 169.229.51.133 169.229.48.1 128.32.44.10 169.229.51.161 169.229.51.226 169.229.51.165 128.32.44.1 Partial Router Connectivity on Millennium Discovered by SNMP
Conclusion • Information collection methods feasible • Automatic discovery • Comprehensive and accurate information about system • Needs user feedback
Future Work • More (or less) features based on user feedback • User interface • More on information analysis and decision making • Fully deploy on millennium