Hydrogen and Fuel Cells
50 likes | 316 Vues
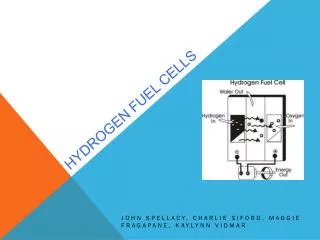
Hydrogen and Fuel Cells. By: Ashley Catrone Vanessa Ritsick Chandel Delucca & Sarah Smith. How does it work?. A fuel cell is an electrochemical energy conversion device. A fuel cell converts the chemicals hydrogen and oxygen into water, and in the process it produces electricity.

Hydrogen and Fuel Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hydrogen and Fuel Cells By: Ashley Catrone Vanessa Ritsick ChandelDelucca & Sarah Smith
How does it work? • A fuel cell is an electrochemical energy conversion device. • A fuel cell converts the chemicals hydrogen and oxygen into water, and in the process it produces electricity. • We are all farmiliar with batteries, they are electrochemical devices. • A battery has all of its chemicals stored inside, and it converts those chemicals into electricity too. This means that a battery eventually goes dead and you either throw it away or recharge it.
Costs and Availability • Statistical data for fuel cell vehicles that are operated under controlled, real-world conditions are very limited and often proprietary. • Current technology does not provide reasonable cost and volume for transportation or stationary applications.
Where is it being used now? • About 9 million metric tonnes of hydrogen are produced in the United States today, enough to power 20-30 million cars or 5-8 million homes. Nearly all of this hydrogen is used by industry in refining, treating metals, and processing foods. Most of this hydrogen is produced in just three states: California, Louisiana, and Texas. • Hydrogen fuel cells (batteries) make electricity. They are very efficient, but expensive to build. Small fuel cells can power electric cars. Large fuel cells can provide electricity in out of the way places with no power lines.
Environment Concerns • New infrastructure • Coal Mining Impacts • Fossil Emissions • Hydrogen Emissions • Vehicle technology pathways