Natural Selection
70 likes | 275 Vues
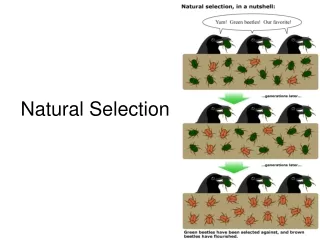
Natural Selection. Charles Darwin’s Big Ideas!. Principles of Natural Selection. There is variation within populations (i.e.; not all penguins or dandelions are alike) Variation is a result of sexual reproduction and mutations in genes More offspring are produced than can live

Natural Selection
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Natural Selection Charles Darwin’s Big Ideas!
Principles of Natural Selection • There is variation within populations (i.e.; not all penguins or dandelions are alike) • Variation is a result of sexual reproduction and mutations in genes • More offspring are produced than can live • There is competition for limited resources • Organisms with the best traits (adaptations) survive and pass on their genes to their offspring
Polar Bear Paragraph • Polar Bears, with their thick layer of fur and fat, are well adapted to cold climates. In terms of evolution and natural selection, how did these changes in the polar bear occur over time?
Polar Bear Paragraph Answer • There is variation among polar bears. Not all polar bears are the same due to genetic differences. Some polar bears are better adapted (just by luck!) to their environment. More polar bears are produced than can survive. There is competition for limited resources. Those polar bears with the best traits, survive and pass on their genes for thick fur and fat to their offspring.
Cave Salamander Paragraph • Cave Salamanders are blind (they have eyes which are not functional). How would a biologist explain how blind cave salamanders evolved from sighted salamander ancestors?
Cave Salamander Answer • There is variation among cave salamanders. Not all cave salamanders are the same due to genetic differences. Some cave salamanders are better adapted (just by luck!) to their environment. More salamanders are produced than can survive. There is competition for limited resources. Blind cave salamanders are able to smell food more easily. Those cave salamanders with the best trait(s) survived and passed on the gene for being blind to their offspring.