Classification
120 likes | 133 Vues
Learn about the system of classification in biology, from Aristotle to Linnaeus, and the benefits of accurately naming organisms. Explore binomial nomenclature, hierarchy, and the use of dichotomous keys in taxonomy.

Classification
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is Classification? • Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities
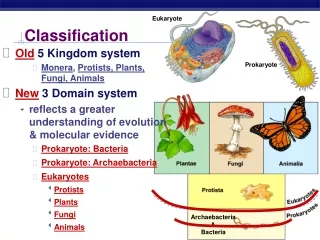
Classification Groups • There is a hierarchy of groups (taxa) from broadest to most specific • The system is as follows: DOMAIN - KINGDOM – PHYLUM – CLASS – ORDER – FAMILY – GENUS – SPECIES
Dumb • King • Phillip • Came • Over • For • Gooseberry • Soup!
Benefits of Classifying • Accurately & uniformly names organisms • Prevents misnomers such as starfish & jellyfish that aren't really fish • Uses same language for all names
Early Scientists • 2000 years ago, Aristotle was the first taxonomist • Aristotle divided organisms into plants & animals • He subdivided them by their habitat ---land, sea, or air dwellers
Linnaeus1707 – 1778 • Classified organisms by their structure • Developed naming system known as binomial nomenclature • Two-word name (Genus & species)
Binomial Nomenclature • First word in the organism’s scientific name is its “genus” Example: pumas, marbled cats, and house cats all classified in the genus “felis.” They share the same characteristics • Genus is always capitalized. • The second word in the organism’s scientific name is “species.” It describes a distinctive feature of the organism. It can mate with each other and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce. • Species is always lower case
Binomial Nomenclature • “Bi” means two • “Nomen” means name • Linnaeus devised a system of naming organisms. Linnaeus placed organisms in groups based on their observable features. Each organism has a unique, two-part scientific name. This naming system is called binomial nomenclature
Binomial Nomenclature • First word in the organism’s scientific name is its “genus” Example: pumas, marbled cats, and house cats all classified in the genus “felis.” They share the same characteristics • Genus is always capitalized. • The second word in the organism’s scientific name is “species.” It describes a distinctive feature of the organism. It can mate with each other and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce. • Species is always lower case
Dichotomous Key • A dichotomous key consists of a series of two part statements that describe the characteristics of an unknown. • At each step the user is presented with two choices. • As the user makes a choice about a particular characteristic of an organism they are led to a new branch of the key. • Eventually the user will be led to the name of the organism that they are trying to identify.