Graph Algorithms 1
40 likes | 160 Vues
Topological sort is a fundamental algorithm used to arrange courses in an order based on their prerequisites. In this directed graph representation, each node represents a course, and each edge (U, V) signifies that U is a prerequisite for V. The objective is to find a linear ordering such that for every directed edge (U, V), U appears before V in the order. This algorithm only works for Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), as cycles prevent a proper ordering. Explore the algorithm through a detailed example to master this essential concept in graph theory.

Graph Algorithms 1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Graph Algorithms 1 http://www.flickr.com/photos/zubrow/6865196143/sizes/o/in/photostream/ Topological sort
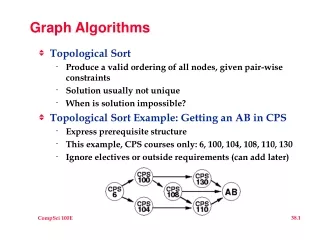
Course Prerequisite Example • Each node is a course • Each edge (U, V) denotes that U is a pre-req for V • Find an order in which these courses can be taken
Topological sort • Topological sort: a linear ordering of vertices such that for every arc (u, v), u comes before v in the ordering • Any linear ordering in which all the arrows go “right” is a valid solution. • Any linear ordering in which an arrow goes “left” is invalid. • Any directed graph with a cycle cannot be topologically sorted
Algorithm module topologicalSort(G) { L ← An empty list S ← A list of all nodes in G with in-degree 0 while S is notempty do • M← S.removeFirst() L.append(M) foreach node N with an edge Efrom M to N do remove edge E from G if N has in-degree 0 then S.append(N) endif endforeach endwhile if the size of G is greater than 0 then return error (G is not acyclic) else return L