Gothic Cathedrals
220 likes | 538 Vues
Gothic Cathedrals. Claire Johnson and Virginia Green. An Overview. Gothic architecture began as a spinoff of Norman design in the 1200s, but rapidly grew and developed a separate identity over the next few hundred years.

Gothic Cathedrals
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Gothic Cathedrals Claire Johnson and Virginia Green
An Overview • Gothic architecture began as a spinoff of Norman design in the 1200s, but rapidly grew and developed a separate identity over the next few hundred years • The massive stone cathedrals took years, money, and labor to build, but they represented a new height of architectural prowess and rich culture
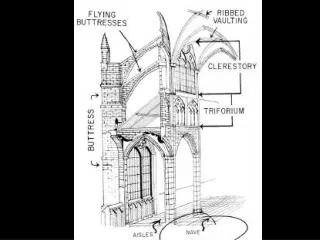
Defining Gothic • Gothic cathedrals represented a significant architectural shift • Gothic architecture tended to be dramatically tall and elaborate; its features were designed to point upwards in praise God • Huge arches and high ceilings made worshippers feel connected to God
Architectural Purpose • The cathedrals were built upon the idea that the worshippers needed to feel close to God • Previous churches were dark, gloomy, and relatively low to the ground • Gothic-style arches and great height were atypical in cathedrals of the time, but they gave church members a new sense of connectedness
Rose Windows • Rose windows were among the most distinctive features of the Gothic style • These huge, circular windows were built on a pattern of stone tracery • The stained glass in between the stone spokes could depict familiar Biblical scenes, but were often simply colorful decoration • These windows served to illuminate and decorate the huge buildings
Flying Buttresses • Flying buttresses were developed for architectural purposes, but soon came to distinguish Gothic art • They were stone extensions from the walls that spread the considerable weight of the cathedral’s walls to the ground • This allowed for taller and heavier cathedrals • They were often ornately decorated as well, and gave the cathedrals a light, upward-sweeping look
Interior Atmosphere • Cathedral interiors were large and breezy due to the spectacular height of the buildings • Stained glass windows prevented them from having a gloomy atmosphere • Huge columns further added to the impression of height • Detailed sculptures and carvings covered the walls
Gargoyles • Gargoyles were an especially memorable feature • These stone heads protruded from the walls all over the outside of the building • The heads were usually grotesque and disturbing, meant to both keep the people properly frightened of demons and to represent the demons themselves • On a practical note, the heads also spat rainwater from the roof
Stonework • The complex carvings that decorated both the interior and exterior of the cathedrals required years of labor and multiple stonemasons • Biblical scenes and figures were recreated in stone • The façade of the cathedral in particular was highly detailed and ornate
Arches • The heavy stone ceilings of the cathedrals required a lot of support, much of which was provided by large pointed arches • The arches spread the weight and prevented the ceilings from collapsing • They were also extremely striking and could be decorative
Vaulted Ceilings • Vaulted ceilings were created by creating a basic framework of stone “vault ribs” to help distribute ceiling weight to the walls • They were similar to arches but did not stand alone • They allowed the ceilings to be unusually high and gave the cathedrals an airy atmosphere
Pinnacles and Turrets • Although flying buttresses shifted weight from the walls, they could push too far sideways and collapse • This was corrected by small but heavy pinnacles, which were essentially small spires • Pinnacles were also aesthetically appealing, contributing to the upward-sweeping theme of Gothic architecture • Turrets were similar, like small towers
Sources • http://chartreslabyrinthtours.com/services • http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fen.wikipedia.org%2Fwiki%2FGargoyle&h=0&w=0&sz=1&tbnid=B1-2lfzLNHl4eM&tbnh=261&tbnw=193&zoom=1&docid=pXaXgioMTbJUSM&ei=spLoUvzUJcnN2wWHsIHQDg&ved=0CAIQsCUoAA • http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.exploring-castles.com%2Fcharacteristics_of_gothic_architecture_2.html&h=0&w=0&sz=1&tbnid=V9QdqUl6kCSSIM&tbnh=194&tbnw=259&zoom=1&docid=ryB6zUw8FrCOYM&ei=spLoUvzUJcnN2wWHsIHQDg&ved=0CAgQsCUoAg • http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Notre_Dame_Cathedral.jpg • http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/gothic_church_architecture.htm • http://www.athenapub.com/14glossary.htm • http://www.exploring-castles.com/characteristics_of_gothic_architecture.html • http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/509828/rose-window • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinnacle