Climate and Climate Science
280 likes | 303 Vues
Explore climate change evidence and the human impact, learn about the climate system's components like the cryosphere, and differences between weather and climate. Discover how interdisciplinary climate science informs our understanding.

Climate and Climate Science
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Climate and Climate Science • Current Weather • Introductions • Is Climate Changing? • Weather vs. Climate • Climate System • Cryosphere For Next Class: Read Chapter 2 (pp. 33-50) Reminder: Labs WILL meet next week!
Introductions • Find out the following information from a partner: • NAME • POINT(S) OF ORIGIN • MAJOR (or projected major) • INTERESTING PLACES VISITED • FAVORITE KIND OF WEATHER • INTERESTS/HOBBIES
Dr. Perry’s Background https://geo.appstate.edu/faculty-staff/faculty/baker-perry https://youtu.be/ISmN0MPR83U http://climate.appstate.edu/~perrylb/Pubs/Media/Andes_Precip_Research_Features_201710.pdf
Global Climate Change Is the climate changing? On what evidence (i.e., what are the indicators of climate change?
Overview of Observed Change Indicators IPCC 2013
Indicators of Climate Change IPCC 2013
Changes in Climate Statistics IPCC 2013
Global Climate Change Do humans have anything to do with climate change? How? Should we care? Is there anything we should do about it?
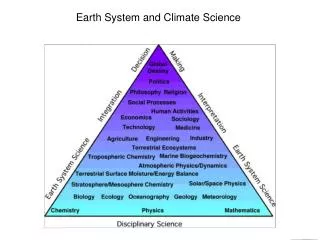
Climate Science • Highly interdisciplinary field drawing on expertise from: • Atmospheric Science • Geography • Chemistry • Physics • Biology/Ecology • Remote sensing and computer science • Economics, Demography, and other social sciences
What is the difference between Weather and Climate? Weather: State of the atmosphere over the short term (minutes to ~15 days). Climate: Synthesis of weather conditions in a given area, characterized by long-term statistics (mean values, variances, probabilities of extreme values, etc.) of the meteorological elements in that area. Climate is what you expect, weather is what you get!
Defining Climate • The Climatic Norm • Encompasses the total variation in the climate record, that is, both averages plus extremes
The Climate System • System: entity whose components interact in an orderly manner according to the laws of physics, chemistry, and biology • Earth’s Climate System: defined as the totality of the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, biosphere and geosphere and their interactions
Atmosphere Relatively thin envelope of gases and tiny suspended particles surrounding the planet Divided into four layers: Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere The Climate System
What is the Cryosphere? Consists of various forms of frozen water at the planet’s surface.
Components of the Cryosphere Snow – a collection of loosely bonded ice crystals deposited from the atmosphere. Sea ice – any form of ice found at sea which has originated from the freezing of sea water. Glaciers – fallen snow that, over many years, compresses into large, thickened ice masses that move. Ice Sheet – mass of glacial land ice extending more than 50,000 square kilometers (20,000 square miles). The Greenland and Antarctic Ice Sheets are the only two that currently exist.
Ice Shelves – thick slab of ice, attached to a coastline and extending out over the ocean as a seaward extension of an ice sheet or series of glaciers. Iceberg – massive piece of ice of greatly varying shape, protruding 5 m or more above sea-level, which has broken away from a glacier and which may be afloat or aground.