Understanding Uncertainty in Numerical Measurements and Compound Naming
50 likes | 169 Vues
This guide explores the concept of uncertainty in numerical measurements, emphasizing absolute and relative uncertainty, and the adjustment of significant figures through proper rounding. It covers essential topics in chemistry, including the naming of polyatomic and diatomic elements, with specific examples like ozone (O3), phosphorus (P4), and sulfur (S8). Additionally, the guide touches on naming binary and ternary compounds, including the need to memorize polyatomic ions and the concept of oxyacids with variable oxygen atoms. Ideal for students and enthusiasts in chemistry.

Understanding Uncertainty in Numerical Measurements and Compound Naming
E N D
Presentation Transcript
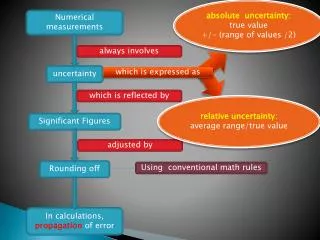
absolute uncertainty: true value +/- (range of values /2) Numerical measurements always involves uncertainty which is expressed as which is reflected by relative uncertainty: average range/true value Significant Figures adjusted by Rounding off Using conventional math rules In calculations, propagation of error
Naming Compounds: Polyatomic Elements • More than two atoms: • Ozone: O3 • Phosphorus: P4 • Sulfur: S8 • Buckminsterfullerene: C60 & C70 • Diatomic Elements • Hydrogen • Nitrogen • Oxygen • Fluorine • Chlorine • Bromine • Iodine
Naming Ternary Compounds: • Polyatomic ions: need to memorize them • Oxyacids: variable number of oxygen atoms