DNA RNA Protein Trait
160 likes | 405 Vues
DNA RNA Protein Trait. Transcription & Translation Chapter 10. R ibo n ucleic A cid. Understanding RNA. Single Stranded. RNA Nucleotides. A. Sugar ( ribose ) B. Phosphate Group C. Nitrogen Bases ( ACGU ). B. A. C. A. Cytosine:Guanine (C G).

DNA RNA Protein Trait
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DNA RNA Protein Trait Transcription & Translation Chapter 10
Ribonucleic Acid Understanding RNA Single Stranded
RNA Nucleotides A. Sugar (ribose) B. Phosphate Group C. Nitrogen Bases (ACGU) B A C
A. Cytosine:Guanine (C G) RNA has Uracil (not Thymine) Rules for Base Pairing in RNA:: B. Adenine:Uracil (A = U)
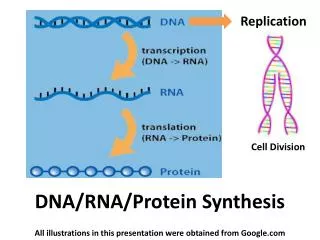
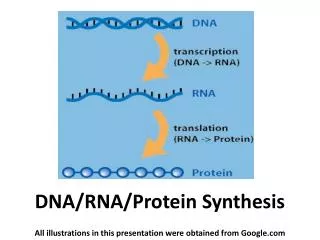
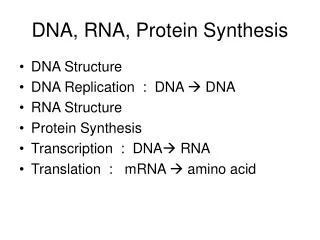
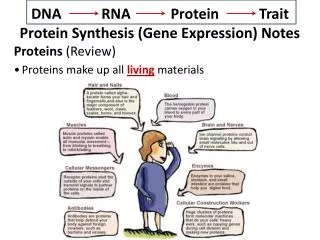
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA RNA Protein Trait 1. Transcription 2. Translation
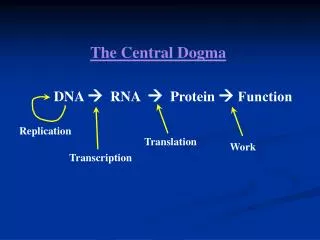
Transcription • In the nucleus • Makes a copy of DNA into mRNA (messenger RNA) • Translation • Happens in ribosome • Ribosomes are in the cytoplasm and on Rough ER • Uses instructions on mRNA to make protein
Transcription: DNA to mRNA • RNA polymerase binds to DNA. • DNA unwinds and separates. • Complementary RNA nucleotides are added. Let’s Watch: http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/transcription/movie.htm
Translation: mRNA to protein • Happens in the ribosome in the cytoplasm • Uses instructions on mRNA to make a protein • mRNA codes for an amino acid and tRNA delivers it
The Triplet Code: Codon Chart mRNA is read in sets of three nucleotides called CODONS. Example: AAG Each codon “codes” for an amino acid. Example: Lysine The codons on mRNA give the order of amino acids to make a protein.
Transfer RNA: tRNA • Codon • 3 nucleotides on mRNA • Anti-codon • 3 nucleotides on tRNA • Complementary to the codon • tRNA has anticodon on one side and amino acid on other
tRNA anticodon binds to codon on mRNA and attaches correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain.
Translation Begins with Start codon: Met
Translation Ends with Stop codon:UAG, UAA, or UGA
Let’s watch Translation http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/translation/movie.htm
Ribosome Structure made of rRNA 2 sub-units