Central Processing Unit (CPU)
490 likes | 2.48k Vues
Central Processing Unit (CPU). Central Processing Unit (CPU). ‘Brain’ of the computer Performs the change of data into information Accepts data from any input device, changes this data according to instructions given by the user and send the result to an output device.

Central Processing Unit (CPU)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Central Processing Unit (CPU) • ‘Brain’ of the computer • Performs the change of data into information • Accepts data from any input device, changes this data according to instructions given by the user and send the result to an output device
Explains how computers process data (input- raw text, numbers) into information (output)
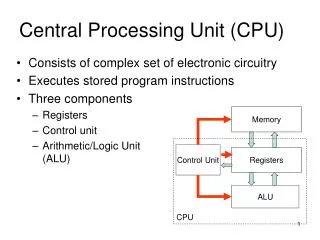
Central Processing Unit (CPU) • Consists of the • Control Unit • Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) • Registers
Control Unit • Directs and coordinates the entire hardware system • Organises the flow of data in a computer • Similar to traffic lights controlling the flow of traffic • It interprets each instruction given by a program and gives appropriate action to be carried out
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) • Performs data calculations including addition, subtraction, division and multiplication • Performs comparisons on data items
Registers • Temporary storage area for small amounts of data or instructions before and after processing. • Some of the different registers are: • Accumulator Register – stores data to be processed • Buffer Register – stores data coming from or being sent to primary storage, e.g printing a document • Address Register – stores location of data in primary storage • Instruction Register – stores the address if the next instruction to be processed
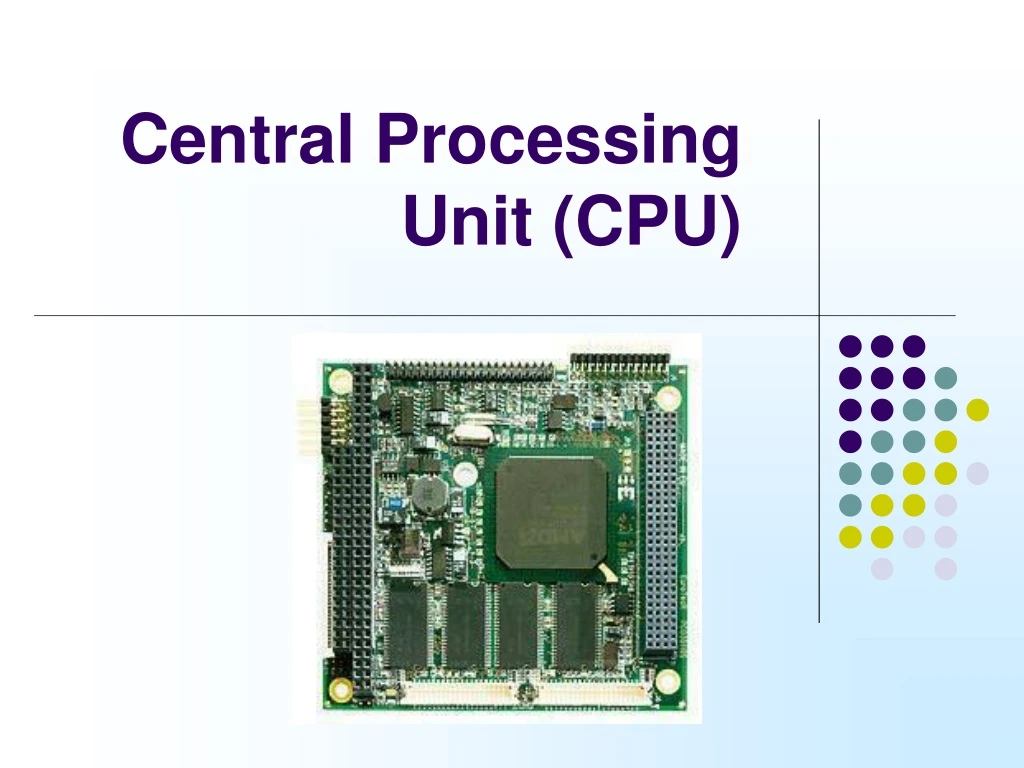
Microprocessor • A central processing unit contained on one integrated circuit • If the processor is built onto a single microchip it is called a microprocessor • Used in PC’s, cameras, DVD players etc.
Development of CPU speeds • Moore's Law - the number of transistors per integrated circuit doubles about once every two years, while the price of the chip remains the same.
Development of CPU speeds • Intel's graph showing growth in the number of transistors over the past 35 years
Central Processing Unit (CPU) Questions: • Describe the role of the CPU. • List and explain the three parts of the CPU • What is a microprocessor and where are they used?