Understanding Cell Structures and Their Functions
180 likes | 310 Vues
This overview explores the essential structures of a cell and their functions. It highlights the importance of the cell membrane in regulating the passage of substances, the protective role of the cell wall in plant cells, and the nucleus as the control center for genetic material. We examine organelles like ribosomes for protein synthesis, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus for substance transport and packaging, lysosomes for waste disposal, and mitochondria and chloroplasts for energy conversion and photosynthesis.

Understanding Cell Structures and Their Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
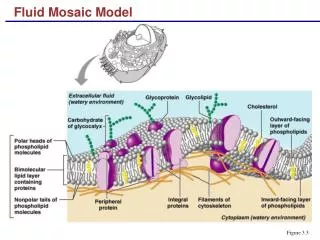
Cell membrane • Contols what enters and leaves the cell. • Semi-permeable or selectively permeable - lets some molecules in and keeps some molecules out lipid layer lipid layer protein
Cell Wall • Protects and maintains the shape of plant cells
Tim & Moby Cell Structures • http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/dl/free/0078695104/164155/00035804.html
Nucleus • Controls cell activities, contains heredity material like DNA • Contains DNA – blueprint for new cells • Nuclear membrane- surrounds the nucleus, keeps heredity material in. • Nuclear pores- openings in nuclear membrane that allow materials to move into and out of nucleus
Nucleolus • Site of ribosome production • Found in nucleus
Cytoplasm • Jelly-like material, the substance inside a cell where organelles are found, cellular reactions occur here found between cell membrane and nucleus
Cytoskeleton Microtubule Microfilament • Functions in support, locomotion, structure, and movement within the cell • Made of microtubules & microfilaments
Microtubules • Hollow tubes that strengthen and maintain the shape of a cell; used in movement
Microfilaments • Tiny filaments that strengthen and maintain the shape of a cell; also used in movement.
Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis (where proteins are put together & made)
Endoplasmic reticulum-canals • System of membranous canals used to transport substances within the cell • Rough ER • Smooth ER
Golgi apparatus • Stack of membranes • Packages substances in the cell, especially secretions, sends to final destination
Vacuole • Plants- protects and maintains shape of plant. • Store materials water, waste,salts, proteins, and carbs
Lysosomes (animals only) • Contains digestive enzymes that are used to remove waste and damaged substances from the cell. • Aka: “suicide sac”
Mitochondria • Site of cellular respiration • Converts food into usable ENERGY • Aka “Powerhouse” • Mighty, Mitochondria
Chloroplast • Site of photosynthesis • Plants only • Contains chlorophyll. A pigment