Cooling System Functions
1.66k likes | 3.56k Vues
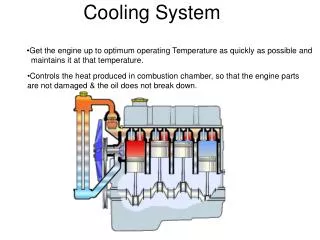
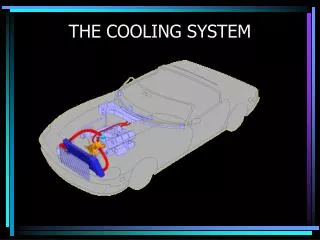
Cooling System Functions. Cooling System. Two types Air Cooled Liquid Cooled. Air Cooled Engines. Advantage Low production cost Disadvantage Vehicle motion is required to keep cool. Air cooled Engines. Finned cylinders Why

Cooling System Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cooling System Functions
Cooling System • Two types • Air Cooled • Liquid Cooled
Air Cooled Engines • Advantage • Low production cost • Disadvantage • Vehicle motion is required to keep cool
Air cooled Engines • Finned cylinders • Why • Creates more surface area to transfer heat away from the engine • Two stroke engines create more heat because they fire on every revolution • Fan • Not used on all engines • Creates air flow past cylinders to transfer heat • Allows engines to run while standing still
Functions of Coolant • Functions of coolant • Dissipate heat • Prevent rust and corrosion • Lubricates the water pump • Prevent Freezing
Protected with antifreeze Water only Corrosion Protection
Liquid Cooled Engines • Advantages • More consistent operating temperature • More precise engine clearances
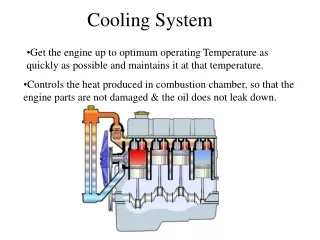
Remove Engine Heat • Combustion can reach 4500 ºF • This is hot enough to melt metal parts • Cooling system removes excess heat
Maintain Operating Temperature • 180 ºF to 210 ºF (80 ºC to 100 ºC) • When an engine warms to operating temperature, parts expand • Ensures that clearances are correct • Ensures proper combustion, minimum emissions, and maximum performance
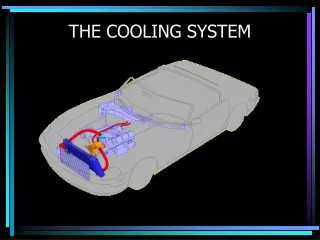
Liquid Cooling Heat is transferred to cylinder wall, into coolant and carried away
Types of Coolant • Green • Ethylene glycol based coolant • Invented in 1926 • Toxic • Two ounces of ethylene glycol antifreeze can kill a dog, one teaspoon can be lethal to a cat, and two tablespoons can be hazardous to children.
Types of Coolant • Red • Dexcool • propylene glycol based • Non-toxic at low levels • Protects aluminum components • Prevents cavitation • Prevents corrosion and build up that destroys parts
Coolant Types • Yellow • Used by Ford • Blue • Used by Honda
Coolant Types • Global • Neon Green in color • Safe to mix with any other color • For More info see • http://www.peakantifreeze.com/aboutus.html
Coolant Lowers coolant freezing point to about -34 ºF (-37 ºC)
Impeller Pump Coolant is thrown outward by centrifugal force, producing suction in the center of the pump housing
Water Pump Cutaway Seal leakage will drip from vent hole
Visual Inspection Watch for leakage from bleed holes
Visual Inspection Pump shaft should not wiggle or leak
Radiator Hoses Two basic types of radiator hoses
Hose Clamps Three basic types of hose clamps
Radiator Transfers coolant heat to the outside air
Downflow Crossflow Radiator Types
Transmission Oil Cooler Small tank inside one of theradiator tanks
Radiator Cap Pressure Valve • Spring-loaded disk • Normally, water boils at 212 ºF • For each pound of pressure increase, boiling point goes up about 3 ºF • Typical pressure: • 12–16 psi • raises boiling point to 250–260 ºF
Pressure Cap Operation Hot engine
Pressure Cap Operation Cold engine
Flex Fan High rpm cause blades to flex, reducing blowing action
Thermostatic Fan Clutch • Bimetal spring controls clutching action • Cold—clutch slips • Hot—clutch locks
Electric Fans • Turned on by • Temp Sending Unit • PCM • Most common fan found today
Thermostat A temperature-sensitive valve
Chapter 40 Cooling System Testing, Maintenance, and Repair
Coolant Protection Level • Find what type of coolant is in system • Test the Protection level (-20 to -35°F) • Test PH level • Check overall condition of coolant
PH Test • Check coolant for DC volts • Acidic coolant acts as a battery acid • If above 0.5 volts than coolant is acidic
Check for leaks • Hook up pressure tester • Apply 2-3 lbs more pressure than cap will hold • Watch for pressure to drop • Look for leaks
Coolant Flush • Removes rust and scale • Should be done every other year
Cooling System Problems Mineral deposits in water jackets can prevent proper heat transfer
Cooling System Problems A cracked part or blown gasket can allow coolant to leak into the engine oil