Windows 2000 Overview
110 likes | 319 Vues
Windows 2000 Overview. Lecture 1 Hassan Shuja 09/07/2004. Windows 2000 Family. Windows 2000 Family Windows 2000 Professional Up to 2 Processors, 4 GB of RAM Windows 2000 Server Up to 4 Processors, 4 GB of RAM Windows 2000 Advanced Server

Windows 2000 Overview
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Windows 2000 Overview Lecture 1 Hassan Shuja 09/07/2004
Windows 2000 Family • Windows 2000 Family • Windows 2000 Professional • Up to 2 Processors, 4 GB of RAM • Windows 2000 Server • Up to 4 Processors, 4 GB of RAM • Windows 2000 Advanced Server • Up to 8 Processors, 8 GB of RAM, Clustering, Load Balancing • Windows 2000 DataCenter Server • Up to 32 Processors, 64 GB of RAM, Clustering, Load Balancing
Windows 2000 Features • Features • Active Directory • Scalable, Standard-compliant directory service for centralized management of network objects • H/W Support ; Plug and Play • USB Support, automatically detect new H/W • More Configuration Options without rebooting • File and Storage System • NTFS v.5, FAT32/FAT support, File encryption/compression • Security and Authentication • Greatly enhanced, Kerberos compliant authentication
Windows 2000 Server • Server Clustering
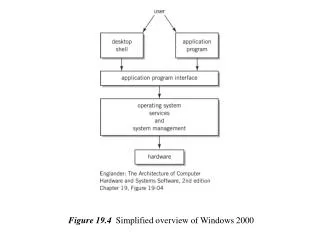
Windows 2000 Architecture • Modular Architecture • Each component/module has sole responsibility for the function it is designed to provide • User Mode and Kernel Mode
User Mode • User Mode • Less privileged processor mode because it does not have direct access to hardware • Limited to assigned memory address space • Uses API to request service from Kernel mode component • Applications and their subsystems run in User mode • 4 types of User mode • Win32 • O/S2 • Posix • Security
Kernel Mode • Kernel Mode • Controls O/S functions, O/S services, and system data and interface to H/W • Kernel mode can directly access hardware and memory • Process not restricted to its own memory • Executive Services provide kernel mode services as requested by application user mode • Kernel Modes • I/O Manager • Window Manager • Microkernel • Device Drivers • HAL
Windows 2000 Memory Model • Memory Model • Virtual memory (paging file) is space on HD treated as if it is RAM • 4 GB of memory – 2GB for Kernel and 2GB for Applications • Virtual Memory Manager manages memory
Workgroup • Workgroup • A group of PCs that are all peers • Resources are usually distributed across all computers • Security is maintained on each computer • Ideal for small groups
Domains • Domains • A Grouping of network devices with a centralized resources and authentication • Centralized user accounts • Domain Controller maintains accounts and permissions • Computers still can have its own User local database • Computers and other resources also need to join the domain • With Windows 2000 no longer a need for PDC and BDC, only Domain Controllers (DC) • Active Directory is maintained on the DC • Provides user logon and authentication • Easy administration • Enables users to easily locate network resources
IP Addresses • IP Addressing • Five classes for IPv4 • Class A,B,C are standard Internet routable addresses • Class D are Multicast addresses • Class E addresses should not be used on Networks and are reserved for research • Private addresses are not Internet routable, used on Intranets • Subnet Masks determines size of local subnet • Default Gateway handles request outside of local subnet