Canada’s Geologic History
150 likes | 430 Vues
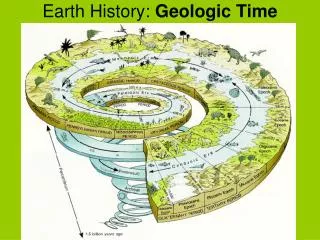
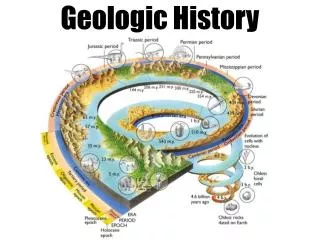
Canada’s Geologic History. The development of Canada’s Landforms. The Canadian Shield Creating The Shield. 3, 500 million years Before Present (B.P.). Cracks in the earth's crust release magma from thousands of volcanos which form the Canadian, Australian, African, and Asian Shields.

Canada’s Geologic History
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Canada’s Geologic History The development of Canada’s Landforms
The Canadian ShieldCreating The Shield • 3, 500 million years Before Present (B.P.). • Cracks in the earth's crust release magma from thousands of volcanos which form the Canadian, Australian, African, and Asian Shields. • Early Canadian Shield as high or higher than Himalaya Mountains.
The Canadian ShieldEroding the Shield • 2, 500 million yrs B.P. • Most volcanic activity ends and a long period of erosion begins. • Wind, water, ice, temperature, and eventually plants erode the Shield and deposit the sediments in the shallow surrounding oceans.
The Canadian ShieldThe Core of Canada’s Landform regions • 1, 000 million yrs B.P. • Hundreds of millions of years of erosion forms thick layers of sedimentary rock surrounding the Shield • The Canadian Shield is worn down to low rounded mountains
The Appalachian MountainsCanada’s Oldest Mountain Chain • Formed approximately 300 million yrs B.P. Pangea was created when all existing landmasses gathered together • Shift of Shield to south and east produces collision with N. Europe and N. Africa • Folding and faulting of sedimentary rock creates Appalachian Mtns.
Great Lakes & St Lawrence LowlandsIncluding Carleton Place • As the Appalachian Mtns are formed the land between the Shield and these Mtns is gently folded. • The Gr Lakes & St Lawrence lowlands have gently rolling hills and wide river valleys. • Today this region is the economic and population heartland of Canada.
The Innuitian MountainsIcy Watch-Towers • Approximately 200 million yrs B.P. Pangea broke apart. • The Shield shifted north and collided with another landmass creating another set of fold Mountains. • The Innuitian Mountains are resource rich but under-developed because of their remote location.
Hudson Bay & Arctic LowlandsA vast and remote land • As the Innuitian Mtns are being created the land between them and the Shield is uplifted creating the Hudson Bay and Arctic Lowlands • These regions are rich in oil, gas, and coal but because the climate is harsh and they are only sparsely inhabited there has been little resource development
Western CordilleraThe Rocky, Columbia, and Coastal Mountain • Approximately 70 million yrs B.P. • Collision of North American and Pacific Plates results in a series of mountain ranges called the Western Cordillera • Folding and faulting, and volcanic activity all played a role in building this youngest Canadian mountain ranges.
Interior PlainsCanada’s Breadbasket • The creation of the Western Cordillera caused the shallow seas covering the prairies to drain. • The Interior Plains have 3 separate levels divided by escarpments. • This region produces vast amounts of cereal crops and is known as Canada’s Breadbasket.