Geologic History
700 likes | 1.07k Vues
Geologic History. This unit will help you develop an understanding of the history of our planet . Formation of the Universe. Big Bang Theory —the most accepted scientific theory of the origin of the universe.

Geologic History
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Geologic History This unit will help you develop an understanding of the history of our planet
Formation of the Universe Big Bang Theory—the most accepted scientific theory of the origin of the universe Def.: Theory that the whole universe began as a dense mass that exploded and expanded outward approximately 13-15 billion years ago * Still expanding today!!! * All the gases and dust from the explosion formed everything in the universe
The Earth is about 4.5 billion years old. That means that approximately 9 billion years went by between the formation of the universe and the formation of the Earth!!!!
Earth began as a big mass of molten material that gradually cooled and hardened
Outgassing The constant volcanic eruptions gave off a great deal of gas
Carbon dioxide Hydrogen Helium Ammonia Methane Sulfur Dioxide Others Outgassing produces early atmosphere consisting of:
Earth was being bombarded with meteorites too!! One was big enough to cause part of the molten Earth to “splash” off and form the moon—and it was really close to us! It has slowly moved farther away Eventually an atmosphere did form and the gases formed clouds and rain (liquid versions of the chemicals listed earlier) began to fall (cooling the hot planet) and made oceans.
Microscopic organisms(bacteria) evolved in the oceans 4.1 billion years ago These organisms eventually evolved the ability to perform photosynthesis (converting sunlight and carbon dioxide into food and giving off oxygen as a waste product) Cyanobacteria 3 billion years ago
Microscopic organisms(bacteria) evolved in the oceans These organisms evolved the ability to perform photosynthesis (converting sunlight and carbon dioxide into food and giving off oxygen as a waste product)
Colonies of Cyanobacteria are called STROMATOLITES. Fossilized stromatolites have been found all over the world
Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Oxygen A few billion years of evolution produced plants and other organisms that turn carbon dioxide into oxygen through photosynthesis. CO2 + sunlight energy (food for plant) + oxygen
This new oxygen production changed our atmosphere and harsh environment into the earth we live in today!
Geologic Time Scale Mainly on the basis of fossil evidence, geologists have been able to break down geologic time into divisions. Fossil -the remains or evidence of something once living Use the ESRT!!! There is A TON of information crammed onto pages 8 & 9 Also…you must remember that MOST sedimentary rocks form in the water and that MOST invertebrate organisms lived in the water
Evolution—by studying fossils, paleontologists (scientists who study fossils) make observations, finding patterns in life forms and theorize that organisms have changed throughout geologic history
Evolution—by studying fossils, paleontologists (scientists who study fossils) make observations, finding patterns in life forms and theorize that organisms have changed throughout geologic history Sweet Video – A Brief History of Life on Earth
How much time is represented by each of these little boxes? 100 million years How much time is represented by each of these larger boxes? 500 million years
Tells us how long ago all the events on this timeline occurred. How long ago was 4600 mya? 4,600 million years ago How many zeroes in a million? 4,600,000,000 years ago
Precambrian Majority of time on Earth 4,600 - 542 = 4,058 mya mya = millions of years ago or 4,058,000,000 years 88% of Earth’s history! Earth’s beginning
What part of the Precambrian is when the oceanic oxygen first entered the atmosphere? Early Proterozoic The oldest known rocks are from what time period? Early Archean or early Precambrian
IMPORTANT: The timeline on the left side of this line is VERY different from the time line on the right side of this line. Please make this line extra dark and bold in your ESRT!!!
youngest Paleozoic Lasted from 542 mya to 251 mya oldest
Indicates the end of the Cambrian period Indicates the beginning of the Cambrian period
The next column (EPOCH) breaks periods down into smaller frames of time. Cenozoic epochs have names whereas the rest are referred to as early, middle and late. If it is early in a period does that mean it is the beginning or the end?
Between Epoch and Life on Earth, there is an ENLARGED timeline for you.
The next column gives you an idea of the plants and animals present on earth during each time period. During which time period were the earliest birds? Late Jurassic
Bar indicates that there is a complete sediment record for the Quaternary period. In the Neogene, no bar indicates that there is a missing sediment record. Perhaps sediments never formed OR erosion took place.
Further down the chart the symbol changes to the rock record. Bar indicates that there is a rock record for the END of the Triassic period and the BEGINNING of the Jurassic period.
This next section gives a bar graph of different groups of fossils. How many periods could you find trilobite fossils from? About 7
The letters match the pictures at the bottom of your ESRT. Where you find the letter on the bar helps you to find the period it lived.
Reading the Important Geologic Events in NY column is similar to reading the other columns. Look for what you need then read horizontally across the ESRT to find the information you are looking for (period, era, epoch, or mya). Just remember that the globes shown here do not go across horizontally!! You must follow the arrows.
Evolution—by studying fossils, paleontologists (scientists who study fossils) make observations, finding patterns in life forms and theorize that organisms have changed throughout geologic history
Relative Dating Vs. Absolute Dating Relative Dating refers to the determination of agecompared to other events. Absolute Dating refers to determining the actual age of somethingin years.
oldest youngest
What you have just done is relative dating! Of course, it’s a little bit more difficult than that for a geologist.
Uniformitarianism— ”the present is the key to the past”—the theory that the geologic processes that are occurring today occurred in the same way in the past. Law of Superposition—the oldest rocks are deposited first Youngest rock layer Oldest rock layer (Think: laundry basket!)
Before we learn about the third law, we need review some vocabulary!
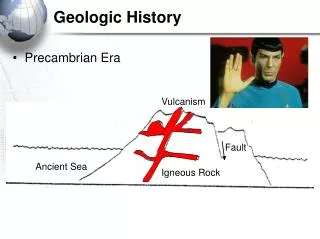
Vocabulary Review Fold—when rock layers are bent/deformed due to tectonic stress (such as plate collisions) “Bent” rock layers are a fold Fault Intrusion of igneous rock Intrusion—when magma cuts through rock, causing contact metamorphism of the pre-existing rock Fault—a crack or break in the rocks along which movement has occurred Extrusion—when magma (lava) cuts through rock and reaches the surface, causing contact metamorphism of the pre-existing rock
Law of Crosscutting Relationships—therocks were there first before anything altered the rock (such as an intrusion, extrusion, fold, or fault) Rocks are older Older Intrusion is younger Fault is younger
Using the two laws you just learned, sequence these rocks. #1 is the oldest. 5 is fault XY 4 6 3 2 1
Law of IncludedFragments—the sediments within the rock are older than the rock itself. Older than the whole rock
Unconformity—a buried erosional surface unconformity http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es2902/es2902page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization
Unconformity—a buried erosional surface unconformity Unconformities form by Deposition of sediments that form rocks Uplift of the rock out of the water Erosion Subsidence—the land sank OR sea level rose so that new rocks could form (repeating the cycle again)
Correlation—matching rocks or geologic events from different places This is important to figure out the geologic events of an area and locating mineral resources. Important for telling the whole story. This can be done by: a.) Index Fossils(see next slide) b.) Volcanic Ash Layers(each volcanic eruption is unique and the chemical properties of the ash are different) c.) Meteorite Deposits (every impact is different and the composition of the meteorites, asteroids or comets is also different and the chemical properties of the debris can be studied)