Unveiling Earth's Ancient History
660 likes | 803 Vues
Rocks hold the story of Earth's past events and life forms. Discover Earth's age, extinction events, and principles of geology. Learn about fossils, geological time divisions, and key geological eras.

Unveiling Earth's Ancient History
E N D
Presentation Transcript
http://www.scotese.com/pangeanim.htm • http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm
Discovering Earth’s History • Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past • We have learned that Earth is much older than anyone had previously imagined.
Warm up 1st wk December • The extinction of a species _____. • A. is a natural event experienced by most species. • B. will never happen in a saltwater environment. • C. cannot occur if a very small gene pool is present. • D. is almost always caused by human activity.
Warm up • The formula for Density (D) is D = m/v. Where m is mass in grams and volume v is in cm3. Solve. The density of a substance is 2g/cm3, the mass is 4 g. What is the volume/ A. 2 CM3 B. 8CM3 c. 2 GRAMS d. 8 GRAMS
Discovering Earth’s History • Principle of Uniformitarianism: The present is the key to the past. • The same forces and processes like volcanism and erosion happening today have been going on for a long time.
Events in Your Life Construct a timeline of the important events in your life. Be sure to include all of the events listed below and any other events you feel are important. Your timeline should be constructed TWO ways: • Numerical Order (use actual dates) • Sequential Order (oldest at left, most recent at right) • ___When you started second grade • ___When you were born • ___ When you started kindergarten • ___When you learned to ride a bike. • ___ When you learned to walk. • ___ When you learned to read. • ___ When you started middle school. • ___ Today’s date. • ___ When you started high school.
Key Principles • Relative Dating • Tells us the sequence in which events occurred • Law of Superposition- oldest on bottom youngest on top under normal conditions
Law of Superposition • Younger Layers→ • Older Layers→
Fossils: Evidence of Past Life • Fossils • Remains or traces of prehistoric life • Found in sedimentary rock
Fossils: Evidence of Past Life The principle of fossil succession states that fossil organisms succeed one another in a definite and determinable order. Therefore, any time period can be recognized by its fossil content. Index fossils are widespread geographically, are limited to a short span of geologic time, and occur in large numbers.
Fossils: Evidence of Past Life Interpreting Environments • Fossils can also be used to interpret and describe ancient environments.
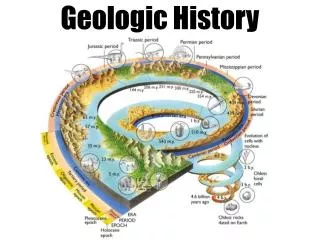
The Time Line Divisions • Oldest Most Recent • Eons Eras Periods Epochs • There are two Eons: • Precambrian and Phanerozoic • Precambrian is both an Eon and an Era • bya – billion years ago • mya – million years ago
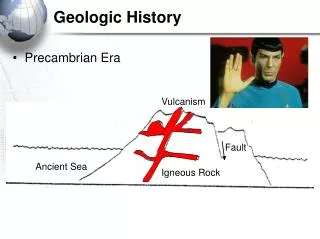
Precambrian Era • All time between origin of Earth 4.6 bya and 540 mya • Rocks lack fossils • Volcanic origin • Igneous Rocks • Basalt, Granite, Obsidian
The First True Cells • Still no oxygen. • The first cells would have lived in extreme environments like the deep sea volcanic vents. • Archaebacteria
Paleozoic Era • Much of the limestone quarried for building and industrial purposes, as well as the coal deposits of western Europe and the eastern United States, were formed during the Paleozoic. • The Cambrian (beginning) opened with the breakup of the world-continent Rodinia and closed with the formation of Pangaea, as the Earth's continents came together once again. • This event is thought to have caused the climate changes that led to mass extinction event. • The Appalachian mountains were formed during this time.
Paleozoic Era • At the end of the Paleozoic, the largest mass extinction in history wiped out approximately 90% of all marine animal species and 70% of land animals. • Possible causes of this Mass Extinction Event • Lowering of sea levels when the continents were rejoined as Pangaea (convergent boundary) • Increased volcanic activity (ash and dust) • Climate changes – cooler climate
Paleozoic Era Youngest, 250 MYA PERMIAN • The Paleozoic Era is divided into 6 Periods CARBONIFEROUS DEVONIAN SILURIAN ORDOVICIAN Oldest, 540 MYA CAMBRIAN
Paleozoic Era • Much of the limestone quarried for building and industrial purposes, as well as the coal deposits of western Europe and the eastern United States, were formed during the Paleozoic. • The Cambrian (beginning) opened with the breakup of the world-continent Rodinia and closed with the formation of Pangaea, as the Earth's continents came together once again. • This event is thought to have caused the climate changes that led to mass extinction event. • The Appalachian mountains were formed during this time.
Cambrian Period • Most of the major groups of animals first appear in the fossil record. • "Cambrian Explosion“ • Trilobite: index fossil • Marine animals
Brachiopods • Marine animals that resemble clams.
Ordovician Period • Increase in number & KINDS of animals • All life in oceans, no land life yet. • Early mollusks, clams
Silurian Period • Similar life to Ordovician • Plants begin to appear on land • Mosses
Devonian Period • “Age of Fishes” • Warm oceans • Land plants multiplied • True ferns • Seed plants • First forests Deer Isle, Maine
Carboniferous Period • Huge freshwater swamps • Coal beds along Mississippi river • 1st reptiles appeared • More insects • “The age of Cockroaches”
Permian Period • Dry Climate • Many sedimentary rocks form • Inland coral reefs created
Mesozoic Era • The Mesozoic Era is divided into three periods CRETACEOUS Youngest, 64 MYA JURASSIC TRIASSIC Oldest, 250 MYA
Mesozoic Era – Middle Life • At the beginning of this era the continents were joined as Pangaea. • Pangaea broke up around the middle of this era. • Reptiles became the most abundant animals because of their ability to adapt to the drier climate of the Mesozoic Era. • Skin maintains body fluids • Embryos live in shells
Mesozoic Era • Dinosaurs were also very active in this era. • First small dinosaurs appeared in the Triassic Period. • Larger and more abundant dinosaurs appeared in the Jurassic Period. • Small mammals and birds also appeared during this era. • The mammals were small, warm-blooded animals. Hair covering their bodies. • These characteristics help them survive in changing environments.
Mesozoic Era • This era ended with a mass extinction event about 65 million years ago. • Many groups of animals, including the dinosaurs disappeared suddenly at this time. • Many scientists believe that this event was caused by a comet or asteroid colliding with the Earth.
Mesozoic Plants Flowering plants evolved towards the end of the Mesozoic Era.
Triassic Period • Extinction of many marine animals • More gymnosperms, pine trees • Earliest dinosaurs
Jurassic Period • Largest Dinosaurs • Primitive birds • Early Primates
Cretaceous Period • Earliest flowering plants • Dinosaurs rule, then mass extinction of dinosaurs • More mammals appear