Phase Changes
110 likes | 455 Vues
Phase Changes. Phase Change. Phase Change: Reversible physical change that occurs when substance changes from one state to another Energy is either released or absorbed during phase changes. 1. Melting. Phase change from Solid to liquid Energy is absorbed by substance

Phase Changes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
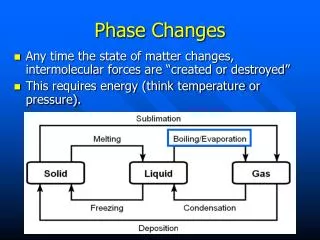
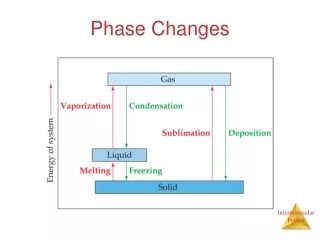
Phase Change • Phase Change: Reversible physical change that occurs when substance changes from one state to another • Energy is either released or absorbed during phase changes
1. Melting • Phase change from Solid to liquid • Energy is absorbed by substance • Heat of fusion: amount of heat energy needed to melt a substance • Varies for different substances
Melting ice Melting iron
2. Freezing • Phase change from liquid to solid • Energy is released from substance • Ex: Milk to ice cream
3. Vaporization • Phase change from a liquid to a gas • Energy is absorbed by substance • Heat of Vaporization: amount of heat energy required to change a substance from a liquid to gas • varies for different substances
Vaporization (2 Types) • 1. Evaporation: Change from liquid to gas at temperatures below the substance’s boiling point • Ex: Evaporating water from ocean • 2. Boiling: Change from liquid to gas at the substance’s boiling point.
4. Condensation • Phase change from gas to liquid • Energy is released from substance
5. Sublimation • Phase change from solid directly to gas (skips liquid phase) • Energy is absorbed by substance • Ex: Dry ice (solid CO2)
6. Deposition • Change from gas directly to solid • Energy is released by substance • Ex: Frost on car windows