South Asia
550 likes | 1.22k Vues
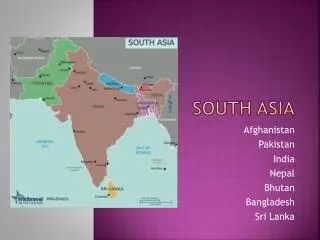
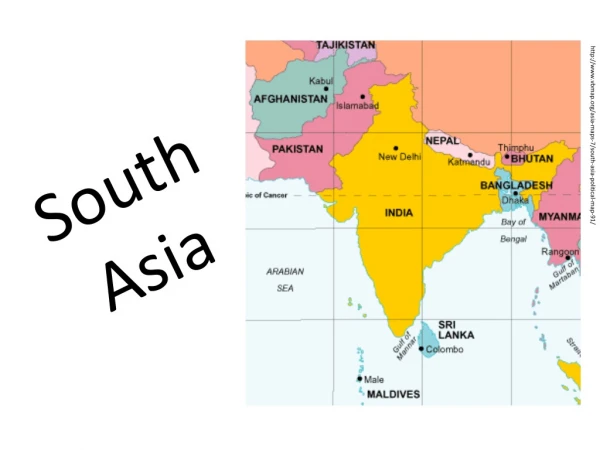
South Asia South Asia Cultural Awareness SCIS Documentaries and Student Presentations Guided Discussion Addressing U.S. Interests South Asia Overview Background People, Culture and Religion Economic and Social Issues Politics and Government South Asia An Overview South Asia

South Asia
E N D
Presentation Transcript
South Asia • Cultural Awareness • SCIS Documentaries and Student Presentations • Guided Discussion Addressing U.S. Interests
South Asia Overview • Background • People, Culture and Religion • Economic and Social Issues • Politics and Government
South Asia • Background • People, Culture and Religion • Economic and Social Issues • Politics and Government
South Asian Culture and Religion • South Asia is home to hundreds of ethnic groups and languages • Leads to natural segregation • India alone has 112 languages with more than 10,000 speakers • 33 of these languages have over 100,000 speakers
South Asian Culture and Religion • The link between ethnicity and regionalism in most South Asian states is important • For example • Each of Pakistan's major ethnic groups is regionally based (Punjabi, Sindhi, Pushtun, Baloch)
South Asian Culture and Religion • Ethnic groups and languages (continued) • India's state borders are principally drawn along ethno linguistic lines • In Sri Lanka, Tamil (Tammel) peoples in the northeast differ from the island's majority Sinhalese population. • Also, various ethnic groupings cross over state borders, such as Tamils (India/Sri Lanka), Bengalis (India/Bangladesh), and Punjabis (India/Pakistan). • Another thing that segregates South Asians
South Asian Culture and Religion • South Asia's caste system, one of the world's oldest surviving forms of social stratification • South Asian society was initially divided into 4 castes • Brahmins (bra-min) (priests and teachers) • Kshatriyas (ke-shat-te)(warriors and rulers) • Vaishyas (vai-sha)(farmers, merchants, and traders) • Sudras (laborers and servants)
South Asian Culture and Religion • A fifth group, called the Candalas were forerunners of the fifth caste also referred to as “untouchables” or by the modern term Dalit meaning “the oppressed” • These people were social outcasts, with bad karma because of sins in past lives. They were given the most unclean and menial tasks, and were the precursors of today's "untouchables."
South Asian Culture and Religion • While South Asian society was never truly divided into these four categories, a hierarchical social system did develop, centered on the principles of strict intragroup marriage and social stratification. • Men and women had to marry within the group into which they were born, perform its occupations, and live by its codes
South Asian Culture and Religion • Governments across the region have outlawed the caste system and initiated many affirmative action efforts, similar to the affirmative action efforts found in the United States Kocheril Raman Narayanan Former Indian President— member of Dalit caste • Many confuse caste status with economic status
South Asian Culture and Religion • South Asian societies are divided in other ways as well • The urban-rural divide is significant, with over 70 percent of South Asians living in rural areas • The countryside is generally more distinguished than cities by complex social hierarchies tied to ethnicity and caste • One thing that tends to unite all South Asians is family
South Asian Culture and Religion • In the United States, family life generally centers on the nuclear group-the mother, father, brothers, and sisters • In much of South Asia, family life is centered on the extended clan, with several generations including uncles, aunts, and cousins living together in the same, adjoining, or nearby dwellings
South Asian Culture and Religion • Family honor is extremely important. • The elderly are respected and cared for. • South Asian parents almost always arrange the marriages of their children, with caste, ethnicity, and class considerations playing prominent roles. • Marriages exist more as a relationship between families than as a love connection between two individuals.
South Asian Culture and Religion • Males dominate family life throughout the region • Women have influence in family affairs, but men head the household, expecting respect and obedience • Several countries in the region follow the Islamic practice of purdah (purda), the traditional seclusion or veiling of women • Women are also subordinate in areas outside the home
South Asian Culture and Religion • Women in much of South Asia face significant harassment, discrimination, and even slavery • Often, they are considered inferior and a family liability • Women often are denied education, access to health care, and jobs outside the home. • They sometimes are thrown out of the house if they do not bear children • Violence against women is common
South Asian Culture and Religion • Female infanticide • Selective abortions • 74 million “missing women” Some things are changing for the better
South Asian Culture and Religion • Today, parliamentary and local government seats are reserved for women across much of the region, and other legal provisions have been enacted • Sri Lanka, India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh have all had female prime ministers Indira Gandhi India Benazir Bhutto Pakistan • While castes, family and gender are important—religion also • plays a key role in the region
South Asian Culture and Religion • The region is the birthplace of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, and many tribal beliefs. • Religions born elsewhere, including Islam, Christianity, Zoroastrianism, and Judaism, have also taken root in South Asia "In religion, all other countries are paupers. India is the only millionaire." Mark Twain
South Asian Culture and Religion • Hinduism and Islam are by far the region's two most influential religions • Some 63 % of South Asians practice Hinduism, itself a collection of various philosophical traditions • Another 30 percent practice Islam • Buddhism is the dominant religion in Sri Lanka and Bhutan Brahma • Since we’ve discussed Islam and Buddhism in previous lessons, we’ll focus on Hinduism here
South Asian Culture and Religion • Hinduism is the oldest and most popular religion in South Asia today • Most modern-day Hindus believe in a set of general principles • (1) Brahman, the Supreme Consciousness, is timeless, formless, and changeless, • (2) The material world is an illusion, known as maya (my-ya) Brahma
South Asian Culture and Religion • General principles continued • (3) Reincarnation (the theory that individual souls are born over and over again until they merge with Brahman) • (4) The individual soul (Atman) is capable of achieving liberation (moksha) by reuniting with Brahman • (5) Everything in the universe is somehow unified • (6) Tat Tvam Asi- Thou art That- one of the most famous statements in all of Sanskrit literature, which equates Atman with Brahman.
South Asia • Background • People, Culture and Religion • Economic and Social Issues • Politics and Government
Economic and Social Issues • Good News • Since the 1940s, millions have been lifted out of poverty • Life expectancy in the area has almost doubled • India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka have taken significant steps toward slowing their population growth • Female literacy in India has gone from 9 percent to 58 percent
Economic and Social Issues • Bad News • 1/3 of South Asia's 1.4 billion inhabitants live below the international poverty line of $1 a day • 3/4 live on less than $2 a day • Roughly 300 million are undernourished, including half the region's children under five • 2/3 don’t have access to adequate sanitation facilities, the worst showing for any region • South Asia has the world's highest illiteracy rates • The average South Asian lives only 63 years, less than the average age of the inhabitant of any world region except sub-Saharan Africa.
Economic and Social Issues • Agriculture has been the primary economic activity in South Asia for centuries. • Today, some 60% of the region's workers are engaged in agriculture, down from roughly 69% in 1980
Economic and Social Issues • India is the “back office to the world” • Over 50% of the world's Fortune 500 companies, including General Electric, American Express, and Dell Computers, outsource IT operations to India, where they have found that the labor is cheap, errors are few, and productivity is high • Even with all of this growth and investment, the regional economy is still overwhelmed by the size of the population
Health and Environment • Many of South Asia’s most pressing health problems are directly attributable to the area’s huge population • Half the size of the United States, the region has five times as many people, almost a quarter of the world's population • India 1947 -- 350 million • India 2005 -- 1 billion+ • Tens of millions of South Asians lack access to basic health services. The prevalence and spread of diseases such as tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS spark intense concern • Huge population also drives many environmental problems
Health and Environment • South Asia also has enormous environmental problems. • A massive cloud of air pollution hovers over large parts of the region sickening people, altering the climate, and damaging crops • Population pressures, politics, and bureaucratic mismanagement strain water supplies, often already heavily polluted and breeding grounds for disease
South Asia • Background • People, Culture and Religion • Economic and Social Issues • Politics and Government
Politics and Government • No single form of government predominates in South Asia • The region's eight states include: • 2 established democracies (India and Sri Lanka) • 1 struggling democracy (Bangladesh) • 2 authoritarian states (the Maldives and Pakistan) • 2 monarchies (Bhutan and Nepal) • 1 elected-but-foreign-backed government struggling to control its own territory (Afghanistan).
South Asia Summary • Background • People, Culture and Religion • Economic and Social Issues • Politics and Government
South Asia • SCIS Videos and Student Presentations
South Asia • Politics and Government • SCIS Video • Student Presentations
South Asia • Politics and Government • SCIS Video • Student Presentations
South Asia • Economics • SCIS Video • Student Presentations
South Asia • Economics • SCIS Video • Student Presentations
South Asia • Population, Health, Environment, and Conflict • SCIS Video • Student Presentations
South Asia • Population, Health, Environment, and Conflict • SCIS Video • Student Presentations
South Asia • Culture and Society • SCIS Video • Student Presentations