Understanding Depth-First Search (DFS) Algorithm in VLSI Design Automation
500 likes | 758 Vues
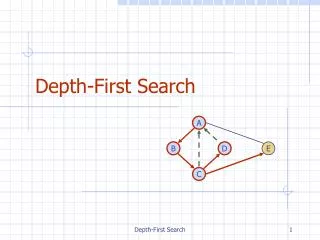
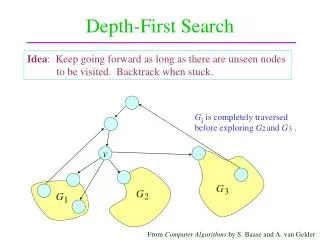
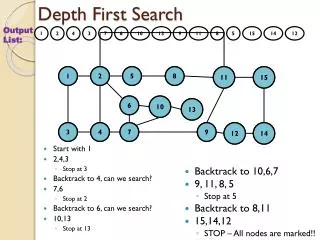
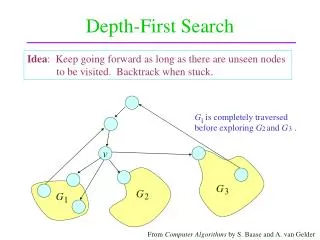
This document provides an in-depth exploration of the Depth-First Search (DFS) algorithm, a fundamental traversal method used in graph theory and VLSI design automation. The DFS algorithm marks each visited node and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. We detail the process through examples, showing how to implement DFS for various scenarios, ensuring that each node is processed efficiently. The insights offered here are tailored for students and professionals seeking a deeper understanding of graph algorithms in the context of VLSI design.

Understanding Depth-First Search (DFS) Algorithm in VLSI Design Automation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
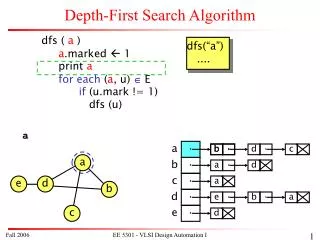
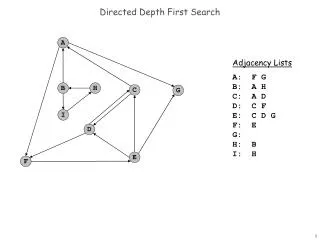
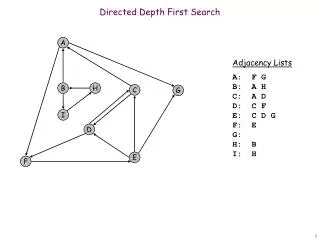
b d a c d d a b b e a · · · · · · · · · · · a a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( a ) a.marked 1 print a for each (a, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
e a d a c d d b a b b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( a ) a.marked 1 print a for each (a, u) E if (b.mark != 1) dfs (b) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... u=b a a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
d a c d d b a e b a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( b ) b.marked 1 print b for each (b, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... a b a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
e a d a c d d b a b b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( b ) b.marked 1 print b for each (b, u) E if (a.mark != 1) dfs (a) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... u=a a b a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
c d a e b b d a d a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( b ) b.marked 1 print b for each (b, u) E if (d.mark != 1) dfs (d) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... u=d a b a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
e a d a c d d b a b b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( d ) d.marked 1 print d for each (d, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... a b d a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
c a a d b b d d b a e · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( d ) d.marked 1 print d for each (d, u) E if (e.mark != 1) dfs (e) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... u=e dfs(“e”) .... a b d a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
c d a e b b d a d a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( e ) e.marked 1 print e for each (e, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... dfs(“e”) .... a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
c a a d b b d d b a e · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( e ) e.marked 1 print e for each (e, u) E if (d.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... u=d dfs(“e”) .... a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
c d a e b b d a d a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( e ) e.marked 1 print e for each (e, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... dfs(“e”) .... a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
c d a e b b d a d a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( d ) d.marked 1 print d for each (d, u) E if (b.mark != 1) dfs (b) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... u=b,a a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
e a d a c d d b a b b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( d ) d.marked 1 print d for each (d, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... dfs(“d”) .... a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
d a c d d b a e b a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( b ) b.marked 1 print b for each (b, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“b”) .... a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
d a c d d b a e b a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( a ) a.marked 1 print a for each (a, u) E if (d.mark != 1) dfs (d) dfs(“a”) .... u=d a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
b d a c e d d b a a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( a ) a.marked 1 print a for each (a, u) E if (c.mark != 1) dfs (c) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“c”) .... u=c a b d e a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
d a c d d b a e b a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( c ) c.marked 1 print c for each (c, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“c”) .... a b d e c a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
e a d a c d d b a b b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( c ) c.marked 1 print c for each (c, u) E if (a.mark != 1) dfs (a) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“c”) .... u=a a b d e c a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
d a c d d b a e b a b · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( c ) c.marked 1 print c for each (c, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... dfs(“c”) .... a b d e c a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
d d a c b e b b a a d · · · · · · · · · · · a e d b c Depth-First Search Algorithm dfs ( a ) a.marked 1 print a for each (a, u) E if (u.mark != 1) dfs (u) dfs(“a”) .... a b d e c a · b · c · d · e · EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 v2 v4 14 5 Edges examined v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 16 v2 v4 14 5 updated, min picked v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 16 v2 v4 14 5 S Augmented v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 16 v2 v4 14 5 Edges examined v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 25 updated, min picked v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 25 S Augmented v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 25 Edges examined v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 25 updated, min picked v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 25 S augmented v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 25 Edges examined v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 20 updated, min picked v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 20 S augmented v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 20 Edges examined v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 20 updated, min picked v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Dijkstra’s Algorithm - an example u0 0 8 v5 v1 10 18 8 16 13 6 9 v6 v7 7 11 17 13 15 v2 v4 14 5 20 S augmented v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1} Node v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 - 2 4 3 - v1 v1v1- EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1} Node v1v2 v3 v4 v5 - 2 4 3 - v1 v1v1 - EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2} Node v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 - 2 4 3 - v1 v1v1 - EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2} Node v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 - 2 1 25 - v1v2v2 v2 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2} Node v1 v2v3 v4 v5 - 21 25 - v1 v2v2 v2 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2, v3} Node v1 v2v3 v4 v5 - 21 2 5 - v1 v2v2 v2 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2, v3} Node v1 v2v3 v4 v5 - 21 12 - v1 v2v3v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2, v3} Node v1 v2v3v4 v5 - 2112 - v1 v2v3 v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2, v3, v4} Node v1 v2v3v4 v5 - 211 2 - v1 v2v3 v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2, v3, v4} Node v1 v2v3v4 v5 - 211 2 - v1 v2v3 v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I
Prim’s Algorithm Example 2 v2 1 5 2 v3 4 2 v5 v1 3 1 3 v4 S = {v1, v2, v3, v4, v5} Node v1 v2v3v4v5 - 211 2 - v1 v2v3 v3 EE 5301 - VLSI Design Automation I