Endocrine System
460 likes | 2.1k Vues
Endocrine System. Functions Sends messages to control and coordinate the body’s environment such as: body temperature metabolism development reproduction Maintains homeostasis and regulates other organ systems Hormones : chemical signals that travel through blood

Endocrine System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
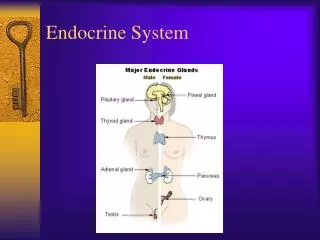
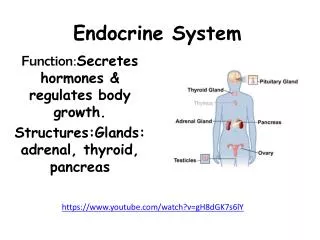
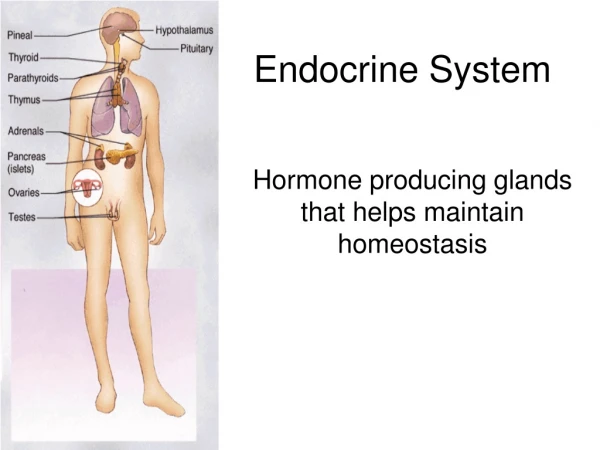
Endocrine System • Functions • Sends messages to control and coordinate the body’s environment such as: • body temperature • metabolism • development • reproduction • Maintains homeostasis and regulates other organ systems • Hormones : chemical signals that travel through blood • Gland : organ that manufactures and secretes hormones • Major Structures • Hypothalamus • Pituitary gland • Many other endocrine glands
Excretory (Urinary) System • Functions • Removes wastes from blood • Regulates concentration of body fluids • Major Structures • Kidneys ** filters blood • Urinary Bladder ** stores urine • Ureters • Urethra
What Happens to the Waste? • When about 200mL urine fill the bladder it stretches and a nerve impulse is sent to the brain signaling the need to go • If you ignore the warnings, bladder gets filled to 400mL then sends an urgent message to the brain • If you keep ignoring the warnings, once you get to 600mL, you lose voluntary control (but you are probably beyond caring at that point! ;)
Integumentary System • Functions • Protects against injury, infection and fluid loss • Helps regulate body temperature • Major Structures • Skin • Nails • Hair
Your skin is the largest organ in the body. Function of Skin: Protective barrier against pathogens Nervous Sensation: contains nerve ending which allows you to communicate with your external environment to sense pain, heat, cold, pressure Temperature Control : blood supply to skin can be altered to adjust heat loss & fat cells under dermis provide insulation Evaporation Control : water resistant barrier Excretion of Waste : carbon dioxide and other waste lost through skin through diffusion or sweat Two Layers of Skin Epidermis • Protective layer • Produces Vitamin D – Essential • for bone development Dermis • Inner layer made up of connective, • nervous & muscular tissue
Lymphatic (Immune) System • Functions • Defends against pathogens and disease • To remove excess fluid, waste, debris, and toxins from cells and tissue spaces • Major Structures • Lymphatic vessels • Lymph nodes • White blood cells • Skin
Lymphatic System and Circulatory System Working Together • Lymph originates as plasma (fluid portion of blood) • Some of this plasma leaves blood stream and flows into the surrounding tissues (called interstitial fluid). • Interstitial fluid delivers nutrients to the cells and takes up cell waste • 90 percent of this tissue fluid flows back through the circulatory system, 10 percent of the fluid is left behind and is now known as lymph • Lymphatic system is designed so lymph only flows upwards (from the extremities), where it is filtered through lymph nodes on its way towards the neck where it re-enters the bloodstream
The Muscular System • Functions • Moves limbs and trunk • Moves substances through body • Provides structure and support • Major Structures • 600 muscles in the human body • Skeletal muscle tissue • Smooth muscle tissue • Cardiac muscle tissue • Muscles can pull but cannot push so many muscles arranged in pairs that work against each other to make joints move • Flexor - muscle that contracts to bend a joint • Extensor - muscle that contracts to straighten a joint
Nervous System • Functions • Regulates behaviour • Maintains homeostasis • Regulates other body systems • Controls sensory and motor functions • Major Structures • Brain • Spinal Cord • Nerves • Sense organs
What is the Nervous System? • The control system that enables animals to detect a stimulus and coordinate a response • Stimulus: changes in the body that are detected by your body • Response: your body’s reaction to this stimulus
How Does Communication Occur? Neurons Nerve cells are called neurons • The functional unit of the nervous system • Use electrical signals called impulses to communicate with other cells • Nerve • a bundle of neurons
Reproductive System • Functions • Produce gametes • male: spermatozoa (sperm) • female: oocytes (eggs) • Produce offspring • Major Structures • Male • Testes • Penis • Female • Ovaries • Uterus • Breasts
Respiratory System • Functions • Moves air into and out of lungs • Controls gas exchange between blood and lungs • Major Structures • Mouth/nose • Trachea • Bronchi • Lungs (consists of alveoli)
Air Pathway • air enters through the nostrils(air is filtered by nose hair) ↓ • nasal cavity (air is warmed, humidified, and sampled for odors) ↓ pharynx ↓ larynx ↓ trachea (aka windpipe)↓ bronchi (there are 2, each leads to 1 lung) ↓ bronchioles ↓ alveoli(clusters of air sacs with very large surface area, surrounded by capillaries), oxygenated blood moves towards the heart, via the pulmonary vein and gets pumped into the left atrium
The lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Your lungs allow you to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. It is connected to a large dome shaped muscle called the diaphragm and to the chest cavity (thoracic cavity) by the pleura. pleural fluid, a lubricating liquid allows the lungs to move smoothly as they passively expand and recoil while you breathe.
Gas Exchange • Occurs at the alveolus • O2 and CO2 have only to diffuse through 2 thin walls: capillaries and alveoli • O2 that we breathe in diffuses from the alveoli into the blood stream and CO2 leaves the blood stream through the alveoli and the air we breathe out
To properly understand the mechanism of breathing, it is necessary to understand • some basic principles about how gases behave. • Gases move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. • Therefore, when the internal pressure is less than atmospheric pressure, gas is • drawn inwards in inspiration (breathing in). • When the internal pressure is greater than the atmospheric pressure, gas is • expelled on expiration (breathing out).
Located in the nasal passage and lungs are small hair like structures called cilia. They serve as a filtration system, removing dust and unwanted particles from the respiratory system Healthy Lung Smokers Lung
Skeletal System • Functions • Protects and supports the body and organs • Interacts with skeletal muscles • Mineral storage • Produces red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in bone marrow (long and flat bones) • Major Structures • Bones (adult human: 206 bones) • Ligaments • Cartilage