Scientific Inquiry: From Curiosity to Theory
140 likes | 194 Vues
Explore the concept of inquiry and the scientific method, from asking questions to testing theories with objective and repeatable evidence. Learn how hypotheses evolve into theories through observation, testing, and revision. Discover the importance of scientific evidence and the process of deductive reasoning.

Scientific Inquiry: From Curiosity to Theory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
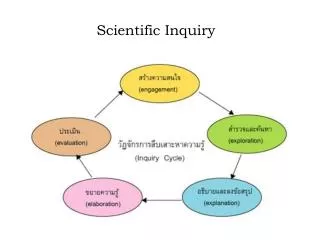
What inquiry means • Learning by asking questions is called inquiry. • An inquiry is like a crime investigation in that there is a mystery to solve. With a crime, something illegal happened and the detective must figure out what it was. Solving the mystery means accurately describing what actually happened
A scientific theory is a human attempt to describe a natural law. • For example, if you leave a hot cup of coffee on the table eventually it will cool down. Why? There must be some natural law that explains what causes the coffee to cool. • A good place to start looking for the answer is by asking what it is about the coffee that makes it hot. • Whatever quality creates “hot” must go away or weaken as the coffee gets cool (Figure 1.15). The question of what heat is — not how to create it or what it feels like but what it is — puzzled people for a long time.
How theories are tested againstevidence • 1. The current theory correctly explains the new evidence. This gives us more confidence that the current theory is the right one. • 2. The current theory does not explain the new evidence. This means scientists must revise the theory or come up with a completely new one that explains the new evidence as well as all the previous evidence, too.
Vocabularies • hypothesis - an unproved or preliminary explanation that can be tested by comparison with scientific evidence. Early hypotheses are rarely correct and are often modified as new evidence becomes available. • theory - a scientific explanation supported by much evidence collected over a long period of time.
When is evidenceconsideredscientific? • The two most important characteristics of scientific evidence are that it be objective and repeatable. “Objective” means the evidence should describe only what actually happened as exactly as possible. • “Repeatable” means that others who repeat the same experiment the same way observe the same results. Scientific evidence must pass the tests of both objectivity and repeatability.
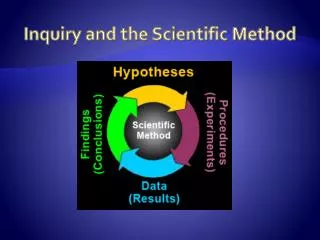
Vocabulary • scientific method - a process of learning that begins with a hypothesis and proceeds to prove or change the hypothesis by comparing it with scientific evidence.
The Scientific Method • 1. Scientists observe nature, then invent or revise hypotheses about how things work. • 2. The hypotheses are tested against evidence collected from observations and experiments. • 3. Any hypothesis which correctly accounts for all of the evidence from the experiments is a potentially correct theory. • 4. A theory is continually tested by collecting new and different evidence. Even a single piece of evidence that does not agree with a theory causes scientists to return to step one
Assignment (question 1-3) • 1. Which of the following is an example of deduction? • a. Hector calls the weather service to find out if the temperature outside is below freezing. • b. Caroline looks out the window and concludes the temperature is below freezing because she sees that the puddles in her neighbor’s driveway are frozen
Question 2 • 2. To be correct, a scientific theory must be everything except • a. supported by every part of a large collection of evidence, • b. believed by a large number of reputable people, • c. testable by comparison with scientific evidence, • d. an explanation of something that actually occurs in the natural world or human technology
Question 3 • 3.Julie, a third grade student, believes that the moon disappears on certain days every month. Explain why the following information is or is not scientific evidence which can be used to evaluate Julie’s hypothesis. • a. Julie sometimes cannot see the moon all night even though the sky is clear. • b. Anne, Julie’s older sister, thinks the phases of the moon are caused by the moon’s position in its orbit around the Earth