Scientific Inquiry
180 likes | 602 Vues
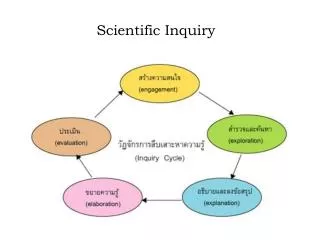
Scientific Inquiry. All Science Is Based Upon Scientific Inquiry. General Steps of Scientific Inquiry. There is no such thing as the scientific method! But, all Scientfic Inquiry includes: Observations/Questions Hypotheses Testing Hypotheses Analyzing Data Drawing Conclusions.

Scientific Inquiry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Scientific Inquiry All Science Is Based Upon Scientific Inquiry
General Steps of Scientific Inquiry • There is no such thing as the scientific method! • But, all Scientfic Inquiry includes: • Observations/Questions • Hypotheses • Testing Hypotheses • Analyzing Data • Drawing Conclusions
MythBusters: A Lesson in Controlled Experiments • Watch the following 8 minute clip of a MythBusters episode. • As you watch, write down how Jamie and Adam apply the steps of scientific inquiry. • http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=97E10867-EF28-450D-8222-7B9EEA6552FA&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US
Testing Hypotheses • Scientists test hypotheses by running CONTROLLED experiments. • In experiments, scientists study factors called independent and dependent variables to find cause and effect relationships.
Independent Variable vs. Dependent Variable • Independent Variable: • The condition or variable that is manipulated by scientists to determine its effect on the dependent variable. • The “Cause” • Graphed on the x-axis. • Dependent Variable • The variable that is measured by a scientist to study the effect of the independent variable. • Graphed on the y-axis • The “Effect” • What is being measured
Smithers thinks that a special juice will increase the productivity of workers. He creates two groups of 50 workers each and assigns each group the same task (in this case, they're supposed to staple a set of papers). Group A is given the special juice to drink while they work. Group B is not given the special juice. After an hour, Smithers counts how many stacks of papers each group has made. Group A made 1,587 stacks, Group B made 2,113 stacks. Identify the: 1. Independent Variable 2. Dependent Variable
Experimental Group vs. Control Group • The experimental group is the group that is being tested and receives the experimental treatment. • The control group is used as a standard of comparison and does not receive the experimental treatment.
Krusty was told that a certain itching powder was the newest best thing on the market, it even claims to cause 50% longer lasting itches. Interested in this product, he buys the itching powder and compares it to his usual product. One test subject (A) is sprinkled with the original itching powder, and another test subject (B) was sprinkled with the Experimental itching powder. Subject A reported having itches for 30 minutes. Subject B reported to have itches for 45 minutes. Identify the-Control Group Independent Variable Dependent Variable
Only ONE Independent Variable can be tested at a time. • All factors (called constants or controls) are kept the same between the experimental and control groups, EXCEPT for the variable being tested. • This is the Independent Variable!!
Analyzing Data • Scientists analyze data to determine if hypothesis is supported or rejected by the data. • Models: graphical/mathematical representation of data. • There are two types of Data: • Quantitative Data: numerical data and objective in nature (for example, there are 9 dolphins). • Qualitative Data: descriptions in words of what is being observed (The dolphins have smooth skin).
Identify the following as qualitative or quantitative data: • The males of a the species are larger than the females. • The hummingbirds in the forested area spent 23% of the time feeding. • The males’ bills are shorter and less curved than those of the female. • There are 32 females and 22 males that live in the forested area.
Practice Problems: • Students of different ages were given the same jigsaw puzzle to put together. They were timed to see how long it took to finish the puzzle. • Identify the variables in this investigation: independent, dependent, controls.
What was the Independent Variable? • Ages of the students • Different ages were tested by the scientist
What was the dependent variable? • The time it took to put the puzzle together • The time was observed and measured by the scientist
What was controlled? • Same puzzle • All of the participants were tested with the same puzzle. • It would not have been a fair test if some had an easy 30 piece puzzle and some had a harder 500 piece puzzle.
The greater the amount of soap in a soap and water mixture, the bigger a soap bubble can be blown. • Design an investigation to test this hypothesis. • Identify the variables • What exactly will be changed? How will it be changed? • What exactly will be measured? How will it be measured?
The farther a ball drops, the higher it will bounce. • Design an investigation to test this hypothesis. • Identify the variables • What exactly will be changed? How will it be changed? • What exactly will be measured? How will it be measured?