Understanding Blood Groups and Immune Responses
160 likes | 271 Vues
Learn how antigens on erythrocytes trigger immune responses, how blood groups are defined by antigens, and the significance of Rh factors in transfusions and pregnancies.

Understanding Blood Groups and Immune Responses
E N D
Presentation Transcript
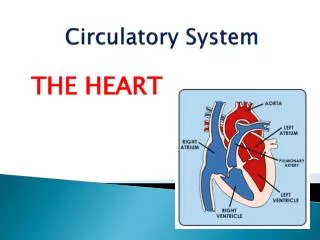
Circulatory System Blood Groups
Immune Response • Antigens on the surface of erythrocytes allow our body to recognize our own cells • Erythrocytes have up to 30 different antigens on them!
Immune Response cont’d • Antigens stimulate your body to form antibodies • An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large Y-shaped protein produced
Immune Response cont’d • When our body recognizes a foreign antigen, it releases antibodies • Antibodies attach to the foreign cell, and causes • Aglunation • the cells to clump together • Or ‘disables’ the cell until a leukocyte can come eat it.
Immune Response cont’d • A blood transfusion only works if our body thinks the blood is our own. • If it recognizes foreign antigens, it will attack! • This would cause our blood to coagulate (clump)
Blood Groups - Type • Blood Type is caused by antigens A and B • A antigens = Type A • B antigens = Type B • A & B antigens = Type AB • No antigens = Type O
Blood Groups – Type cont’d • Antibodies • Type A blood has • B antibodies • Type B blood has • A antibodies • Type AB has • NO antibodies • Type O • Has A and B antibodies
Blood Groups- Rh Factor • Rhesus Factor • Named for the rhesus monkey in which it was discovered • Based on the ability to MAKE an antigen! • The antigen is not automatically present • Rh positive (Rh+) • can make the Rh antigen • Rh negative (Rh-) • cannot make the antigen
Blood Groups and Transfusions • Blood transfusions must match compatible ABO blood groups and the Rh Factors • O – negative • The Universal Donor • Naked blood, has no antigens! • Does not trigger an immune response from any blood type • O-neg does recognize all other types as foreign though… so can only receive O-neg!
Sharing Blood- Pregnancy • Concerning for women when they are pregnant • Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) • results from Rh incompatibility between an Rh- mother and Rh+ fetus.
Sharing Blood- Pregnancy • In the first pregnancy, some Rh+ blood from the fetus enters the mother's system during birth, causing her to produce Rh antibodies. • The first child is usually not affected • But the antibodies remain in the mother system, causing reactions of the maternal immune system in future pregnancies.
Sharing Blood- Pregnancy • Rh- mothers are given an Rh antigen during the first pregnancy with an Rh+ fetus and all subsequent Rh+ fetuses.
Complete the Chart Complete the chart
Complete the Chart Complete the chart