Accuracy and Precision
300 likes | 818 Vues
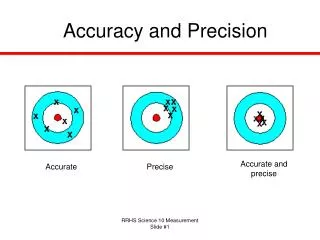
Accuracy and Precision. Accurate and precise. Accurate. Precise. Precision and Measuring. High precision measurements give confidence in the results, since they are reproducible. When using a measuring device, we want to be as precise as is possible with the measuring device.

Accuracy and Precision
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Accuracy and Precision Accurate and precise Accurate Precise
Precision and Measuring • High precision measurements give confidence in the results, since they are reproducible. • When using a measuring device, we want to be as precise as is possible with the measuring device. • This requires estimating.
Measurement Uncertainties • Measurements often fall between markings Example 1 • Rectangle above is between 2 and 3 cm • Best Estimate: 2.3 cm(3 is considered the uncertain digit)
Measurement Uncertainties Example 2 • Rectangle above is between 30 and 40 cm • Best Estimate: 36 cm(6 is considered the uncertain digit)
Check Your Learning What is the measurement indicated in the following images? 3.2 cm 1.40 cm 15.3 cm
Significant Digits • Tells us how many digits are meaningful in a measurement • Last significant digit is always uncertain • All nonzero digits are significant: • 112.6 m has four significant digits • All zeros between nonzero digits are significant: • 108.005 m has six significant digits.
Significant Digits • Zeros at the beginning of a number are NOT significant • 0.07080 has four significant digits. The leading zeros in the number 0.07080 are not significant; they are simply placeholders
Significant Digits • Zeros at the end of a number may or may not be significant • Zeros after the decimal point at the end of a number are significant: • 20.00 cm has four significant digits.
Significant Digits • Zeros at the end of a number where there is no explicit decimal point are NOT significant; they are considered to be placeholders. Often, the rightmost zero which is significant is indicated by a bar placed over it: • 109000 km contains three significant digits; • km contains five significant digits. • If the decimal point is explicitly written, all zeros at the end are significant; • the number 2000. has four significant digits.
Check Your Learning How many significant digits does each of the following numbers have? • 103 • 1.0 • 0.045 • 3200 3 2 2 2
Addition and Subtraction The rightmost figure in the answer will be determined by the leftmost place at which an uncertain digit occurs in any of the measurements being added or subtracted.
Addition and Subtraction • Answer is 325.9, since both 9 and 4 are uncertain.
Multiplication and Division • The product or the quotient should not have more significant digits than the factor which has the fewest number of significant digits.
Multiplication and Division • Only the “7” was obtained using only certain digits • Correct answer is 7800
Complete the following calculations using the proper number of significant digits: Check Your Learning 1330 15 120 9 • 1230 + 95 • 12.0 + 3
Dimensional Analysis • Conversion Factor - a fraction that is mathematically equal to one, used to convert from one unit to another, e.g. • Dimensional Analysis – looking at units in a calculation to see how they must cancel out to give the desired units. This can identify the proper conversion factor to use.
Unit Conversions Example 1: Change 1222 millimetres (mm) to metres (m). Notice that the mm units cancel out in this example, leaving only m as proper unit
Unit Conversions Example 2: Change 95 km/h to m/s. Notice that in this example, both the km and h cancel out, leaving us with the desired units of m/s.
Unit Conversions Example 3: Change 132 mg into kg. Notice that in this example, both the mg and g cancel out, leaving us with the desired units of kg.
Check Your Learning • Convert 34 cm into m. • Convert 12.3 m/s into km/h. • Convert 8.40 km into m. • Convert 13.3 mg into kg 0.34 m 44.3 km/h m kg
Units of Area • Area in cm2 • Length in m • Area in m2 • Rule? • Area in mm2 • Rule? • 100 cm2 • 0.1 m • 0.01 m2 • Factor of 10-4 from cm2 to m2 • 10000 mm2 • Factor of 10-6 from mm2 to m2
Check Your Learning Convert each of the following: • 25 cm2 = ________m2 • 0.42 m2 = ________cm2 • 0.53 m2 = ________mm2 • 420 mm2 = ________m2 • 0.0025 m2 • 4200 cm2 • 530000 mm2 • 0.00042 m2