Understanding Complex Numbers: Square Roots of Negatives and Their Applications
400 likes | 517 Vues
Discover the fascinating world of complex numbers and learn how to take the square root of negative numbers using "i," the imaginary unit. This lesson explores the foundation of complex numbers, their representation in the complex plane, and various operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with complex numbers. Engage with examples illustrating how to apply these concepts in real-world problems. Perfect for high school students in algebra and analytic geometry, this lesson encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.

Understanding Complex Numbers: Square Roots of Negatives and Their Applications
E N D
Presentation Transcript
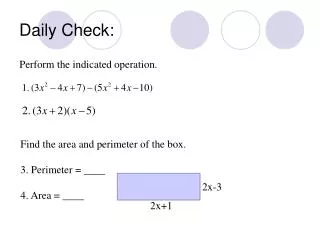
Daily Check: Perform the indicated operation. Find the area and perimeter of the box. 3. Perimeter = ____ 4. Area = ____ 2x-3 2x+1
CCGPS Analytic GeometryDay 32 (9-20-13) UNIT QUESTION: In what ways can algebraic methods be used in problem solving? Standard: MCC9-12.N.RN.1-3, N.CN.1-3, A.APR.1 Today’s Question: How do we take the square root of negative numbers? Standard: MCC9-12..N.CN.1-3
A long long time ago, in a math class far, far away.. There was no way to take the square root of a negative number
Every time we squared a negative number We got a positive.
(-1) = 1 (-2) = 4 (-3) = 9
Was there a number, that when multiplied by itself Gave you a negative???
Can we in fact, take the square root of a negative number? WE CAN!!!!
Ladies and Gentlemen of Math II I present to you a NEW number... A number so complex...
It stretches the imagination.. I present to you:
You can't take the square root of a negative number, right? • When we were young and still in Math I, no numbers that, when multiplied by themselves, gave us a negative answer. • Squaring a negative number always gives you a positive. (-1)² = 1. (-2)² = 4 (-3)² = 9
So here’s what the math people did: They used the letter “i” to represent the square root of (-1). “i” stands for “imaginary” So, does really exist?
*For larger exponents, divide the exponent by 4, then use the remainder as your exponent instead. Example:
$25,000 Pyramid i 1 -i -1 i -i -1 -i 1 -1
$25,000 Pyramid i -i -1 -1 -i i -1 -i 1 -i
Complex Numbers • A complex number has a real part & an imaginary part. • Standard form is: Real part Imaginary part Example: 5+4i
The Complex Plane Real Axis Imaginary Axis
Adding and SubtractingAdd or subtract the real parts, and then, add or subtract the imaginary parts. Ex: Ex:
MultiplyingTreat the i’s like variables, then change any that are not to the first power Ex: Ex:
Conjugates: Two complex numbers of the form a + bi anda – bi are complex conjugates. The product is always a real number Ex:
Conjugates: Two complex numbers of the form a + bi anda – bi are complex conjugates. The product is always a real number Ex:
Conjugates:Two complex numbers of the form a + bi anda – bi are complex conjugates. The product is always a real number
Dividing Complex Numbers • Multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator. • Simplify completely.
Assignment Complex Numbers Practice WS