Diffusion and Osmosis
140 likes | 172 Vues
Explore osmosis and diffusion processes, understand cellular respiration equation, identify organelles involved in protein synthesis, and learn the effects of water on cells. This educational guide provides links to animations and experiments to enhance understanding.

Diffusion and Osmosis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
TSWBAT identify the process of osmosis and diffusion via the gummi bear lab-analyze diffusion through a sand baggie and apply the concepts of hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic to the activity • On a blank sheet of paper • Write the equation for cellular respiration. • Where does cellular respiration occur in the cell? • List the organelles that help to make proteins • What is the difference between the rough and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
1 4 2 3 Diffusion • Solvent – what dissolve something • Solute – what is being dissolved • Solute molecules moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Random motion drives diffusion • Movement is based on kinetic energy (speed), charge, and mass of molecules • Equilibrium is reached when there is an even distribution of solute molecules • http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html (water)
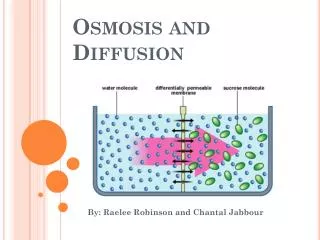
Osmosis • Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane • Semi-permeable: permeable to solvents (WATER), but not to large molecules • High [water] to low [water] • Dissolved molecules (i.e. glucose, starch) are called solutes • REMEMBER: Water = solvent Glucose, Starch = solutes http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_works.html
Effect of Water on Cells • Hypertonic Environment • High [solute], low [water] • The cell will shrink • Plasmolysis – cell death Hypotonic Environment • High [water], low [solute] • Plants – turgor pressure – plant like this!! • Animals – cytolysis – cell bursting • Isotonic Environment • [water] = [solute] Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Part 3 pg. 85
Cellulose in cell wall Osmosis in Living Cells
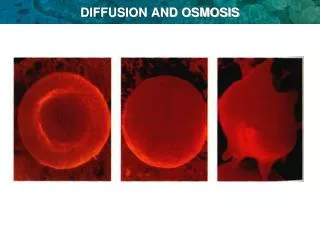
Isotonic Predictions? Hypertonic Hypotonic Osmosis in Red Blood Cells • 0.9% saline • 10% NaCl • Distilled water Plasmolysis
Hypertonic Predictions? Hypotonic Osmosis in Plant Cells Plasmolysis • . • 10% NaCl • Distilled water
Animations Dialysis Bag Experiment • http://ccollege.hccs.cc.tx.us/instru/Biology/AllStudyPages/Diffusion_Osmosis/Baggif.swf Elodea Cell • http://ccollege.hccs.cc.tx.us/instru/Biology/AllStudyPages/Diffusion_Osmosis/Elodeagif.swf Osmosis • http://ull.chemistry.uakron.edu/genobc/animations/osmosis.mov
Transportation of Molecules • Passive Transport • Movement of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane • no energy required • Active Transport • Movement of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane against a concentration gradient with a protein • ENERGY – ATP • Facilitated Diffusion • Movement of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane with a protein • no energy required