Understanding Diffusion and Osmosis: Key Concepts and Processes
270 likes | 436 Vues
This guide covers essential concepts of diffusion and osmosis, crucial processes in cellular biology. Diffusion is the movement of substances from areas of high to low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. This detailed overview provides examples of how substances like glucose, oxygen, and carbon dioxide move in and out of cells, exploring how these processes affect cell health. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for comprehending how cells interact with their environment, maintain equilibrium, and perform necessary functions.

Understanding Diffusion and Osmosis: Key Concepts and Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Diffusion and Osmosis SQA questions
W hat you should know - diffusion G • In diffusion, a substance will move ( d_____) from an area of h_____ concentration to an area of l__ concentration • Dissolvedf___, o_____, c_____ d_____ and w_____ enter and l_____ the cell by diffusion • Diffusion allows the e_________ of m________ e.g. o_______ and g________ move intocells and carbon dioxide moves o___ iffuse igh ow ood xygen arbon ioxide ater eave xchange C aterials xygen lucose ut
enter diffusion Glucose and oxygen _______ by diffusion ___________ leaves the cell by _________ carbon dioxide
The cell membrane c______ diffusion – the passage of substancesi____ and o__ of the c___ The cell membrane is s_________ permeable – s______ molecules can pass through the p_____ in the membrane ontrols nto ut ell electively mall ores membrane = glucose starch = = water
What you should know - osmosis • Osmosis is a s______ case of d_______ • In osmosis w____ molecules move from a h___ w____ concentration to a l__ w____ concentration across a s__________ permeable membrane e.g. the cell m_________ or v______ t_______ pecial iffusion ater igh ater ow ater electively embrane isking ubing
Examples of osmosis If a cell(X) with 5% glucose solution is surrounded by a 10% glucose solution(Y), in which direction will osmosis occur ? 1 X Watermoves ____ of cell from ___ to ____ because X has ___ % water (HWC) and Y has ___ % water (_____) out Y = 10%glucose Y 95 X = 5% 90 LWC
2 If cell(A)with 2% salt solution is next to a cell(B) with 1% salt , in which direction will osmosisoccur ? Water diffuses from cell B _____to cell A ____ by__________. Cell B has____% water Cell A has _____% water. HWC LWC osmosis A = 2% salt B = 1% salt 99 98 3 equal In plant cells X and Y there is an ______concentration water (___%) and therefore there is no net or ________ movement of water i.e. water ___ = water ___ 95 X = 5% SALT overall Y = 5% SALT in out
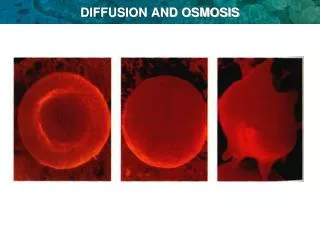
Osmosis in plant cells Water e_____ the cell by o______. Vacuole swells up and cell becomes t______. The c___ w____ prevents b________ enters C smosis urgid cell all high water concentration ursting same water concentration No change Water ___ = Water in out W_____ leaves the cell by osmosis. Vacuole s______ and the m_________ is pulled a___ from the cell wall. Cell is p__________. ater low water concentration hrinks embrane way lasmolysed
Osmosis in animal cells e.g. Red Blood Cells Animal cell behave differently due to the absence of a _______ C cell wall Animal cells gain water by ________ ________and ________ osmosis swell up burst high water concentration ___________ water ___ = water ___ no change same water concentration in out low water concentration b Cells _____ water by _______ and ______ lose shrink osmosis
high concentration low concentration
Dissolved food oxygen carbon dioxide
Cell membrane osmosis
atmosphere Muscle cells diffusion osmosis
0.9 No gain or loss of water at this concentration / No osmosis at this concentration / No change to cells at this concentration / They look like the untreated cells Cells have shrunk or crinkled up or shrivelled up Water has moved out of cell to a lower water concentration / Water has moved out of cell down a concentration gradient
osmosis water moved out of cell from a high to low water concentration / water moved to a lower water concentration outside the cell / water moved from a higher water concentration inside the cell oxygen / glucose / amino acid
Shrink and wrinkle Swell up and burst lost higher
allows exchange of materials /allows water to diffuse into root/ allows glucose to diffuse into cell /