Endocrine System
490 likes | 626 Vues
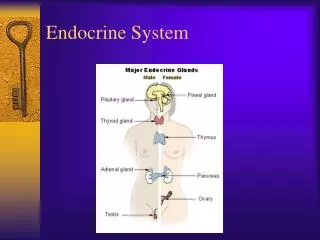
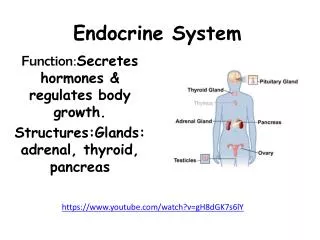
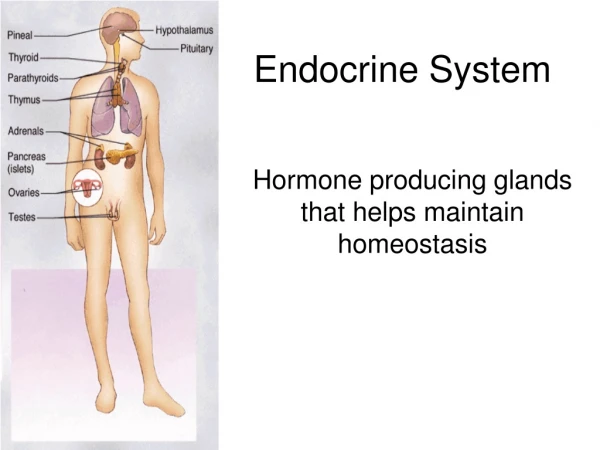
Endocrine System. Spring 2012 FINAL. Endocrine Glands. Pituitary gland Pineal gland Adrenal glands Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Thymus gland Pancreas Gonads Hypothalamus. Pituitary Gland. Anterior FSH LH TSH ACTH PRL MSH Endorphins GH Posterior ADH Oxytocin.

Endocrine System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Endocrine System Spring 2012 FINAL
Endocrine Glands • Pituitary gland • Pineal gland • Adrenal glands • Thyroid gland • Parathyroid gland • Thymus gland • Pancreas • Gonads • Hypothalamus 1
Pituitary Gland • Anterior • FSH • LH • TSH • ACTH • PRL • MSH • Endorphins • GH • Posterior • ADH • Oxytocin 2
Pineal Gland Melatonin 3
Adrenal Glands • Adrenal Cortex • Mineralocorticoids • Glucocorticoids • Androgens • Adrenal Medulla • Epinephrine • Norepinephrine 4
Thyroid Gland • TH • Thyroxine • Triiodothyronine • Calcitonin 5
Parathyroid Gland • PTH 6
Thymus • Lymphocytes • Thymosin 7
Pancreas • Glucagon • Alpha cells • Insulin • Beta Cells 8
Gonads • Females • Estrogen • Progesterone • Males • Testosterone 10
Hypothalamus • TRH • GnRH • GHRH • CRH • Somatostatin • Dopamine 11
Osteoporosis • Classified by age groups • Most common is postmenopausal • Decrease in bone density (subtractive) • Treatment increase calcium and vitamin D in comination with hormone therapy 12
Osteoporosis 13
Osteomalacia • Lack of calcium in the tissues & a failure of the bone tissue to calcify • Caused by malabsorption of fats • If it occurs after growth plate closure it is called Rickets 14
Demonstrates as osteopenia on x-ray. Appears similar to osteoporosis Except for the presence of bands Of radiolucency within the bone Osteomalacia 15
X-ray of affected bones show cortical thickening with a coarse Thickened trabecular pattern Often called “cotton wool” Appearance Mixed areas of radiolucency & radiopaque areas Paget’s Disease 16
Paget’s Disease • Metabolic disorder of unknown cause • Has two stages: • Osteolytic • Osteo blastic • Fairly common in elderly • Affects men twice as frequently as women 17
Acromegaly X-ray demonstrates an enlarged sella Turcica and changes in the skull Obliterates diploe found between inner & outer tables of the cortical bone 19
Acromegaly • Endocrine disorder caused by a disturbance of the pituitary gland • Primarily affects skeletal system • Have a prominent forehead & jaw, widened teeth, abnormally large hands, coarsening of facial features 20
Hypopituitarism • Decreased levels of pituitary hormones • Most common cause is pituitary infarction • Caused by ischemic pituitary necrosis, postpartum hemorrhage, shock, sickle cell disease, meningitis, shock, syphilis, and head trauma • CT, MRI and angiography can be used for radiographic evaluation 21
Hypopituitarism • Short stature with protruding abdomen • Sparse hair • Coarse facial features • Wide-set eyes • Broad nose • Protruding tongue 22
Diabetes Insipidus • Deficiency in vasopressin • Insufficient ADH • Usually secondary to intereference with ADH production • Can be hereditary • Nephrogenic D.I. • Symptomes • Polyuria • Increased thirst • Low urine osmolality • Treatment • Hormone therapy 23
Cushing’s Syndrome http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vxSAhLyKVqw 25
Cushing’s Syndrome • Have a “moon” face with excess fat deposits in neck and trunk • Skin is thin and does not heal well • CT and MRI demonstrates pituitary adenomas 26
Diabetes Mellitus • Syndrome characterized by chronic hyperglycemia is combination with glucose intolerance • Alteration is metabolism of carbs, fats and proteins 31
Type 1 • Produce little to no insulin • Symptoms • Increase urination • Excessive thirst • Increase in appetite • Treatment 32
Type 2 • Inadequate secretion of insulin • More common in women than men • Treatment is similar to DM 1 33
Hyperthyroidism • Autoimmune disorder • Thyroid gland secretes excess amounts of TSH • Enlarged thyroid and protruding eyes • Hyper and nervous • Treatment includes: medical management, surgical resection Administration of radioactive iodine
Hypothyroidism • TH deficiency • Commonly seen in PT’s with Hashimoto’s syndrome • May be caused by iodine insufficiency • Symptoms: • decreased energy levels • hot & cold intolerance • personality changes • weight gain • Treatment is hormone replacement therapy
Hyperparathyroidism X-ray demonstrates osteopenia, especially in the diaphyses of the phalanges and clavicles Pathologic fractures may exist as a consequence of the softened bony matrix
Hyperparathyroidism Disrupts the calcium Phosphate ration and Results in increased Levels of PTH.
Nephrocalcinosis Tiny deposits of calcium dispersed through renal parenchyma Can be seen on an IVU and plain radiographs
Radiography • Useful in diagnosing some disorders • Metabolic diseases of the skeletal system • Cushing's’ • Decrease in CA in osteomalacia & osteoporosis • Disorders of pituitary gland • Changes in sella turcica • Acromegaly
Bone Mineral Densitometry • Determines mineral and calcium content in bone • Can assist in the diagnosis of • Osteoporosis • Osteomalacia
MRI • Useful in evaluating pituitary disorders • Pituitary adenomas • Presence of progress • With Gadolinium • Microadenomas
CT • Useful in diagnosis and follow-up of pituitary disorders • Pineal gland • Neoplastic diseases of thyroid , adrenal glands & parathyroid glands • Enlargement of adrenal glands • Biopsies frequently performed under CT
Nuclear Medicine • Diagnosing thyroid function • Detecting nonpalpable nodules • Evaluate remaining thyroid tissue • After surgical resection or ablation • Localize medullary tumors of adrenal glands • Using radioisotopes to treat this tumor of the medullary portion of the adrenal glands