Mesopotamia
320 likes | 615 Vues
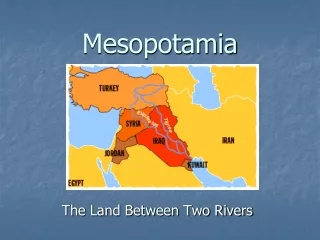
Mesopotamia. Primary Empires. Mesopotamia means “Land between the rivers” Civilization developed between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, in present day Iraq and Kuwait, around 3,000 BCE. Mesopotamia. Sumerians Akkadians Babylonians Hittites Assyrians Chaldeans Phoenicians Israelites

Mesopotamia
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mesopotamia Primary Empires
Mesopotamia means “Land between the rivers” • Civilization developed between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, in present day Iraq and Kuwait, around 3,000 BCE
Mesopotamia • Sumerians • Akkadians • Babylonians • Hittites • Assyrians • Chaldeans • Phoenicians • Israelites • Persians
The World’s First Known Civilization – Sumer3,000 BCE - 2,350 BCE
Sumerians • Inventions • Arch • Dome • Wheel • Writing (cuneiform) • Number system based on 60 • Polytheistic • Theocracy
The Epic • Consider: • What do these films have in common? • Lord of the Rings • Star Wars
The Epic • Meets the following criteria • It is a long verse narrative on a serious subject • Told in a formal and elevated style • Centered on a heroic or quasi-divine figure on whose actions depends the fate of a tribe, a nation, or the human race.
The Epic • Write down as many modern epics that fit this criteria.
The Epic • Traditionally were written versions of oral poems. • Usually about a tribal or national hero during warlike times.
The Epic • Hero is a figure of great national, or cosmic, importance. • Setting is ample in scale • Action involves superhuman deeds in battle or a long, arduous, and dangerous journey. • Gods and other supernatural beings take an interest. • Ceremonial performance and narrated in a ceremonial style.
Epic of Gilgamesh Tablet 11 of Epic of Gilgamesh
Epic of Gilgamesh • Recited orally for centuries • Recorded 2800-3000 BCE • Predates all other major writings of antiquity • Gilgamesh • semi historical figure may have ruled Uruk around 2800 BCE • Two-thirds god; one-third man • Searches for ever-lasting life. • Enkidu (Inn-KEY-Do) • Dearest companion of Gilgamesh • Killed because Gilgamesh spurns affection of the Queen of Heaven, Ishtar
Key Themes: • Peeping Tom: • Window into Mesopotamia • The nature of the relationship between Gilgamesh and Enkidu • Civilization vs. Beast • Friendship • Cultural Difference • Role of Women • Nature of Gods • Importance of Fame / Immortality
Hammurabi’s Code • History’s first known written laws • 282 laws in total • Hammurabi (standing) receiving the laws from Shamash • Where we get the phrase “an eye for an eye”
AssyriansKing Sennacherib • Extremely well organized military and government. • “The land bathed in blood.” • Cruel warriors • Iron weapons
AssyrianContributionsKing Ashurbanipal • Permanent roads • First postal system • First use of mercenaries • Great library at Nineveh had 22,000 clay tablets.
Chaldeans (New Babylonians) • Famous for the Hanging Gardens & Tower of Babel • Most famous King was Nebuchadnezzar • Observations of the sky led to astronomy and astrology.
Persian government became a model for future governments Cyrus & Darius • Established a tax collection system • Allowed locals to keep customs and religions • Built a system of roads that are still used today • Satrep – “governor”
The Persian Religion • Founded by the prophet Zoroaster. • Central theme is a struggle between good an evil. • Concept of heaven (pairidaeza) and hell. • Was taken up by Alexander the Great, the Romans, and future world religions.
Persian empire ended when it was overrun by Alexander the Great in 331 BCE.