The Nervous System
120 likes | 276 Vues
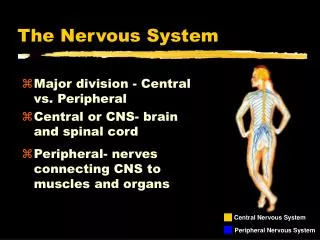
The Nervous System. Vertebrate nervous systems. The nervous system has two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) . The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and acts as a coordinating centre for incoming and outgoing information.

The Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Vertebrate nervous systems • The nervous system has two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). • The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and acts as a coordinating centre for incoming and outgoing information. • The PNS consists of nerves that carry information between the organs of the body and the CNS.
Theperipheral nervous system • The PNS can be further subdivided into somatic and autonomic nerves. • The somatic nervous system has sensory nerves that relay information about the environment to the CNS, while motor nerves initiate a response. • The autonomic nervous system controls the internal organs of the body, and consists of the sympathetic and parasympatheticnervous systems → often operate as “on-off” switches.
Main divisions of the nervous system Nervous System central nervous system peripheral nervous system brain spinal cord somatic nerves autonomic nerves sensory motor sympathetic parasympathetic Voluntary Involuntary
Cells of the nervous system • There are two different cell types found in the nervous system: glial cells and neurons. • Glial cells are nonconducting cells that are important for structural and metabolic support of neurons. • Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. • Neurons are categorized into three groups: sensory, motor, and interneurons.
Anatomy of a neuron • Parts of a typical neuron include: • Dendrites – receive information. • The axon – carries the nerve impulse towards other neurons or to effectors (like muscles, for example). • Many axons are covered with a myelin sheath, which acts as insulation. Myelin is formed by special glial cells called Schwann cells. • The areas between sections of the myelin sheath are called the nodes of Ranvier.
Nerve impulse conduction • Nerve impulses: • Are electrical. • “Jump” from one node to another, increasing the speed of neural transmission. • Move much faster along myelinated nerves than nonmyelinated nerves. • The speed of conduction is also affected by axon diameter – the smaller the diameter, the faster the speed.
Communication between neurons • The transmission of a nerve impulse between two neurons (which occurs at specialized structures called synapses) is typically either electrical or chemical. • Chemical synapses “convert” the electrical signal into a chemical one through the release of neurotransmitters.
Neural circuits • The simplest neural circuit is the reflex arc. • Most reflexes occur without brain coordination. • Reflex arcs contain five essential components: - the receptor - the sensory neuron - the interneuron in the spinal cord - the motor neuron and - the effector