Cell Growth and Division Process
170 likes | 189 Vues
Learn about the limits to cell growth, stages of cell division, chromosomes, mitosis, and cytokinesis in the cell cycle. Explore how uncontrolled cell growth leads to disorders like cancer.

Cell Growth and Division Process
E N D
Presentation Transcript
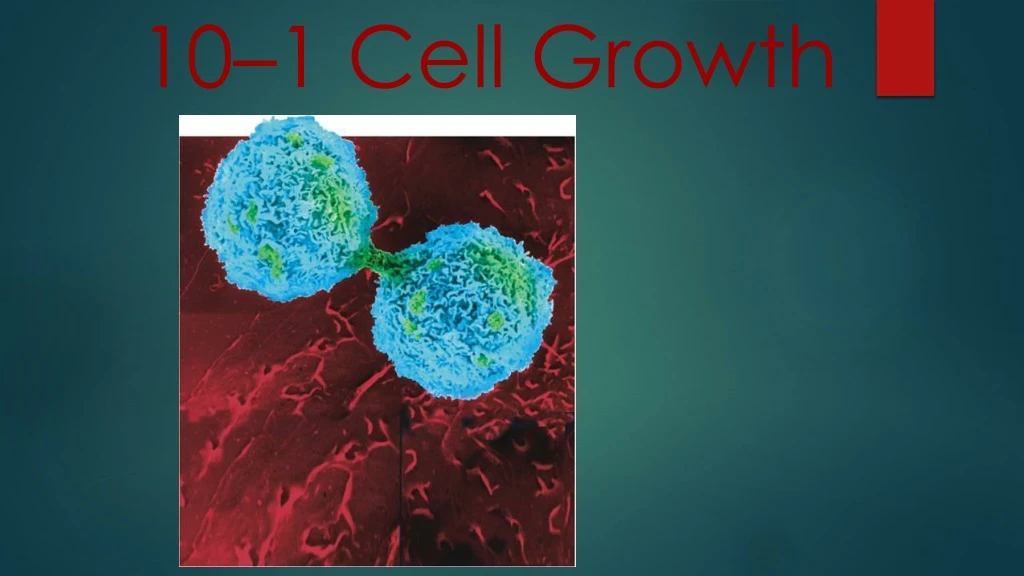
Limits to Cell Growth10 Cell Division • The rate at which food, oxygen, water, and wastes are moved in and out of the cell is dependent on the surface area of the cell and its volume. • The larger a cell is, the longer it takes to get rid of waste and get food.
10 Cell Division C. Cell Growth • In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. • The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. • The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
10 Cell DivisionChromosomes D. Chromosomes • Before cell division, each chromosome is duplicated, or copied. • Each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” chromatids. • Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the centromere.
Events of the Cell Cycle Cell Cycle • Interphase is the period of growth that occurs between cell divisions. It is the most important and longest phase.
The Cell Cycle E. Cell Cycle or Mitosis • The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide.
The Cell Cycle F. Cell Cycle • Interphase • During G1, the cell • increases in size • G stands for growth • During the S phase, • chromosomes are replicated • S stands for synthesis
Mitosis G. Mitosis (PMAT) pee mat • Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases: • Prophase • Prophase is the first and longest phase of mitosis. • The centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. • Metaphase • The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. • Anaphase • The sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes. • Telophase • Chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell and lose their distinct shape.
Mitosis Spindle forming • Prophase Centromere Chromosomes (paired chromatids)
Mitosis Centriole • Metaphase Spindle
Mitosis Individual chromosomes • Anaphase
Mitosis • Telophase
Cytokinesis • Cytokinesis • the cytoplasm pinches in half. • Each daughter cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes
H. In plants, a structure known as the cell plate forms midway between the divided nuclei. Cytokinesis in Plants Cell plate Cell wall
Cell Cycle Regulators I. Cell Cycle Regulators • The cell cycle is regulated by a specific protein called cyclin.
Uncontrolled Cell Growth J. Uncontrolled Cell Growth • Cancer is a disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth. • How are cancer cells different from other cells? Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells.