ENTRY QUIZ
200 likes | 310 Vues
Explore the fascinating element silicon (Si), atomic number 14, which plays a crucial role in modern technology and is widely used in computers. Learn about its properties as a metalloid and its atomic structure, alongside key scientific concepts such as theories, laws, and the scientific method. This entry discusses accuracy and precision in measurements, the nature of systems and feedback loops, and the principles of sustainability encompassing technology and environmental challenges. Delve into the significance of silicon in various scientific and ecological contexts.

ENTRY QUIZ
E N D
Presentation Transcript
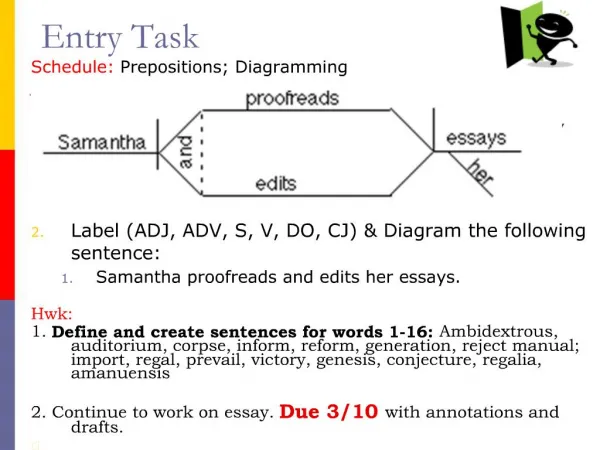
ENTRY QUIZ 1. What is element for today? 2. What properties do you expect? 3. Is it metal? 4. Is it magnetic? 5. What is the next element?
14th element SILICON Si Atomic number 14 Atomic number 28.09 Metalloid, widely used in computers Atomic structure 14 p, 14 e, 14n
Theory and Law • Scientific Theory • A hypothesis that has been supported by multiple scientists’ experiments in multiple locations • A Scientific Law • a description of what we find happening in nature over and over again in a certain way
Scientific Laws • Law of Conservation of Matter • Matter can be changed from one form to another, but never created or destroyed. • Atomic Theory of Matter • All matter is made of atoms which cannot be destroyed, created, or subdivided.
Accuracy and Precision • Accuracy • The extent to which a measurement agrees with the accepted or correct value for that quantity. • Precision • A measure of reproducibility, or how closely a series of measurements of the same quantity agrees with one another.
Reasoning • Inductive Reasoning • Uses observations and facts to arrive at hypotheses • All mammals breathe oxygen. • Deductive Reasoning • Uses logic to arrive at a specific conclusion based on a generalization • All birds have feathers, Eagles are birds, therefore All eagles have feathers.
Scientific Methods • What is the question to be answered? • What relevant facts and data are known? • What new data should be collected? • After collection, can it be used to make a law? • What hypothesis can be invented to explain this? How can it become a theory?
Experiments • Variables are what affect processes in the experiment. • Controlled experiments have only one variable • Experimental group gets the variable • Control group does not have the variable • Placebo is a harmless pill that resembles the pill being tested. • In double blind experiments, neither the patient nor the doctors know who is the control or experiment group.
Systems • A system is a set of components that function and interact in some regular and predictable manner • It has a structure and a function • The earth is a closed system for matter and an open system for energy • Can use models • Graphic, physical, conceptual, mental, mathematical
Feedback Loops • A feedback loop occurs when an output of a system is fed back as an input (two kinds) • Positive loops are runaway cycles where a change in a certain direction causes further change in the same direction • Negative loops occur when a change in a certain direction leads to a lessening of that change
Synergy and Chaos • Synergy occurs when two or more processes interact so the combined effect is greater than the sum of the separate effects • Chaos occurs in a system when there is no pattern and it never repeats itself
Questions • Which procedure is NOT part of the scientific method? • Hypothesis (B) Systematic estimation (C) Analysis (D) Observation (E) Conclusion 2. According to the Atomic Theory of Matter, all matter is made of atoms which cannot be • Created II. Destroyed III. Subdivided (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and II (D) I and III (E) I, II, and III 3. The earth is a ______system for matter and an ______ system for energy • closed; open (B) open; open (C) closed; closed (D) open; closed (E) created; open 4. Which of the following is an example of a negative feedback loop? • Warming that leads to melting of glacial ice which raises sea level • Deforestation which leads to reduced biodiversity which leads to less gene diversity • Agricultural runoffs which leads to water pollution which decreases biodiversity • Temperature sensors on the skin that detect a stimulus • Burning of coal which leads to acid rain which leads to deforestation
Resource Consumption and Environmental Problems • Underconsumption • Overconsumption • Affluenza: unsustainable addiction to overconsumption and materialism.
CULTURAL CHANGES AND THE ENVIRONMENT • Agricultural revolution • Allowed people to stay in one place. • Industrial-medical revolution • Led shift from rural villages to urban society. • Science improved sanitation and disease control. • Information-globalization revolution • Rapid access to information.
SUSTAINABILITY ANDENVIRONMENTAL WORLDVIEWS • Technological optimists: • suggest that human ingenuity will keep the environment sustainable. • Environmental pessimists: • overstate the problems where our environmental situation seems hopeless.
Four Scientific Principles of Sustainability: Copy Nature • Reliance on Solar Energy • Biodiversity • Population Control • Nutrient Recycling Figure 1-16
Implications of the Four Scientific Principles of Sustainability Figures 1-17 and 1-18
TYPES AND STRUCTURE OF MATTER • Elements and Compounds • Matter exists in chemical forms as elements and compounds. • Elements (represented on the periodic table) are the distinctive building blocks of matter. • Compounds: two or more different elements held together in fixed proportions by chemical bonds.
Activity 4 • Name some scientific laws. • What is reasoning? • What is control group? • What is synergy? • What is chaos?
EXIT QUIZ 1.How many elements do you know? 2.What are they? 3.Which of them are inert gases? 4.Which are metals? 5.Which are metalloids?