Digestion
390 likes | 674 Vues
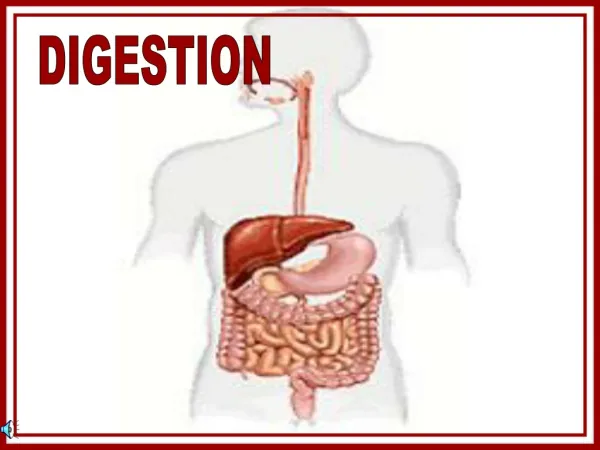
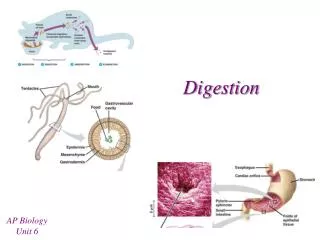
Digestion. I. Introduction. A. Processes. The basic digestive processes Ingestion , Digestion ( mechanical and chemical ), Absorption ( extra-cellular and intracellular ), and Elimination. Figure 41.7. B. Parts Overview.

Digestion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Digestion I.Introduction A.Processes
The basic digestive processes Ingestion, Digestion (mechanical and chemical), Absorption (extra-cellular and intracellular), and Elimination. Figure 41.7
The basic parts tube (alimentary canal, G-I tract, etc.) and a series of glands (salivary, liver, pancreas, etc.) Figure 41.8
II.Development A.Simplest
1. Direct to gastrovascular cavity == Poriferans through Platyhelminthes Poriferans simply absorb molecules gathered from their watery homes. Choanocytes Figure 33.4
1. Direct to gastrovascular cavity == Poriferans through Platyhelminthes Figure 33.10 Figure 41.7
1. Alimentary canal == Nemerteathrough theChordates Figure 41.8 How is food moved through the tube? What forces are involved? Why have the segmentation of the tube?
III.Mammalian A.Tube 1. Sections
a. Oral cavity = ingestion, chewing, & chemical digestion teeth, tongue, buccal surfaces, and salivary glands b. Pharynx = move & lubricating food muscular wall and mucous glands c. Esophagus = move, lubricating food, & peristalsis muscular wall and sphincter d. Stomach = churn food & chemical digestion muscular wall and gastric glands
e. Small Intestine = chemical digestion & absorption Figure 41.12
e. Small Intestine surface area Figure 41.13
f. Large Intestine = water absorption& packing surface area and muscular wall
g. RectalandAnal Canals = packing & elimination muscular wall
B.Glands & Organs 1. Salivary Glands
Salivary Glands = mucin, salivary amylase, buffers, & antimicrobial agents Saliva to coat food, start carbohydratedigestion, control acidity, and prevent infection
Gastric Glands = pepsinogen, HCl, & mucous. Figure 41.11 begin protein digestion, activate pepsinogen to pepsin, and buffer
3. Liver and Gall bladder = secrete or store bile Figure 41.19 emulsifies fat
Pancreas = secrete numerous digestive enzymes Figure 41.12
1. What are the molecules and the mechanism of absorption for each of the ingested nutrient molecules?
D.Regulation 1. Cephalic
Digestion regulation can be divided into the cephalic and the gastric phases? Cephalic phase == nervous response Events: Stimuli related to food starts? Salivary secretions Stimulation of the stomach smooth muscle
Gastric phase== nervous response andendocrine input Events: Stimuli is the stretching of the stomach wall? Release of stomach secretions Pancreatic enzymes Liver/GB bile release Smooth muscle stimulation
IV.Comparisons A.Dentition
Dentitionis adapted to accommodate different diets. Types of teeth = incisors, canines, premolars, & molars Figure 41.16
Tubular divisionsare adapted to accommodate different diets. Figure 41.18 Figure 41.17