1 mV
130 likes | 301 Vues
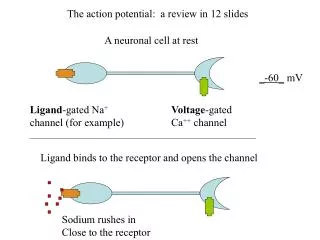
1 mV. familial startle syndrome. Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Alcohol General Anesthetics. Chem. driving force. Elec. driving force. Rasmussen’s Encephalatis. Kainate Receptor. AMPA Receptor. Vc. +. Presynaptic glutamatergic Neuron. Postsynaptic Neuron. Vm = -35 mV.

1 mV
E N D
Presentation Transcript
familial startle syndrome Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Alcohol General Anesthetics
Chem. driving force Elec. driving force
Rasmussen’s Encephalatis Kainate Receptor AMPA Receptor
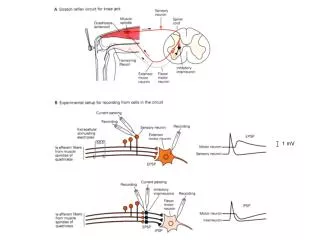
Vc + Presynaptic glutamatergic Neuron Postsynaptic Neuron Vm = -35 mV NMDAR EPSC AMPAR EPSC Vm = -70 mV NMDAR EPSC AMPAR EPSC Glutamate receptor excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs)
ionotropic receptors metabotropic receptors Effector
Ionotropic receptor synaptic actions Metabotropic receptor synaptic actions Indirect Direct slower (0.1-100 s) fast (ms) open or close channels open synaptic channels resting channels, voltage-gated channels, fast synaptic channels channels only at synapse modulate excitability excite or inhibit AP
ACh closure PIP2 PLC Gq DAG IP3 Ca release Protein kinase C
1.5 2. Decrease in slow delayed rectifier K current nA 1. Decrease in resting outward K current 0 1. Slow EPSP