Endocrine System
170 likes | 309 Vues
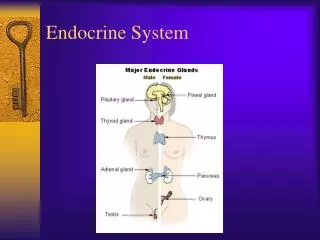
Endocrine System. Lecture 3 Pancreatic gland and its hormones. Asso . Professor Dr Than Kyaw 24 September 2012. The pancreas. Pancreas – both exocrine and endocrine functions Exocrine function - associated with digestion - include digestive enzyme and bicarbonate secretions.

Endocrine System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Endocrine System Lecture 3 Pancreatic gland and its hormones Asso. Professor Dr Than Kyaw 24 September 2012
The pancreas Pancreas – both exocrine and endocrine functions Exocrine function - associated with digestion - include digestive enzyme and bicarbonate secretions
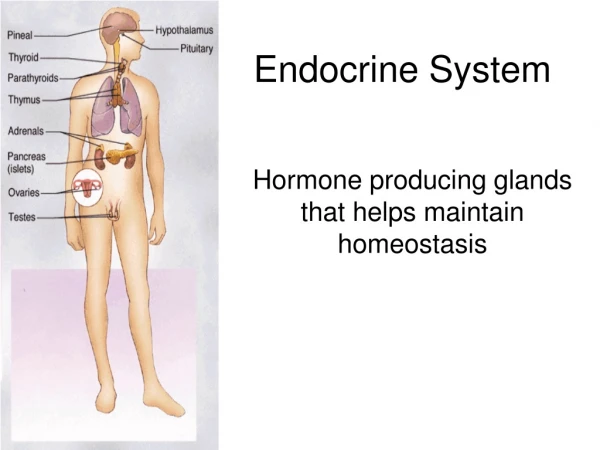
Pancreas and its secretions • - long, thin delicate organ • pinkish gray, glandular • Secretions of pancreas • Exocrine • - enzymes and carbonates • Endocrine • - hormones
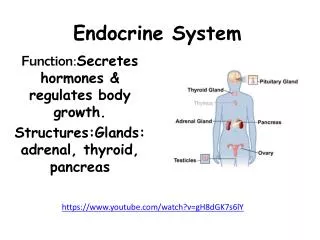
Pancreatic hormones Hormones of the pancreas - Insulin • Glucagon • Somatostatin • Pancreatic peptides • They are secreted by the specific cells located in the islets scattered throughout thte pancreas • polypeptides
Pancreas and its hormones • Endocrine • - islets of Langerhans • 4 types of cells • - insulin ( beta cells) • - glucagon (alpha cells) • - somatostatin (delta cells) • - pancreatic peptides • (F cells)
Pancreas and its hormones • Insulin sensitivity • Liver, muscle, adipose tissue and leukocytes - rapid response • Brain, kidney, intestine and erythrocytes - little or no response • Principle effect on sensitive tissues which allow the transport of glucose across the cell membrane • Insulin enhances facilitated diffusion • Liver – insulin enhances glucose uptake • - by stimulating enzymes that assist production of glycogen and lipogenesis • - by inhibiting enzymes that catalyze glycogenolysis
Pancreas and its hormones • Generally insulin promotes • Fat deposition • Protein synthesis • - The result of insulin activity - lowering blood glucose level
Insulin Blood Glucose Main functions Fat Break down inhibited uptake of glucose Muscle, Liver (Stored as glycogen) Insulin uptake of amino/a Amino acids Used for protein synthesis by all cells Insulin - All essential amino/a (balanced ration) are needed for protein synthesis
Glucagon • The result of glucagon activity - elevation of blood glucose concentration • This is achieved by activation of adenylcyclasein liver cells. • It in turn stimulate s phosphorylase -- result in glycogenolysis. • Glucagon also - increases gluconeogenesis - increases metabolic rate - stimulate lipolysis
Glucagon Glycogen Glycogenolysis Opposite effect of insulin glucagon glucose Fat (Lipolysis) glucagon glucose
Control of insulin and glucagon secretion – Glucose homeostasis
Normal blood glucose value of animals (mg/dl) Blood glucose level lower than other animals
Somatostatin • Inhibitory agent - slow the output of nutrients into the circulation • To moderate the metabolic effects of insulin, glucagon and growth hormone • i.e., somatostatin inhibit s secretion of insulin and glucagon • Also as a moderator it inhibits the secretion of cholecystokinin , pancreatic exocrine secretion and gastric acid • Somatostatin also moderates gastroinstestinal motility and absorption of glucose
Pancreatic polypeptide • The secretion of pancreatic polypeptide - stimulated - by ingestion of protein - by fasting - No definite function has been established
Control of insulin and glucagon secretion • The secretion of insulin and glucagon - controlled directly by the blood glucose concentration • Because of dual control of these two hormones - blood glucose level show little variation Important stimulatory effects of insulin on the secretion of - gastrointestinal hormone, gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, and other hormones, • Gastrointestinal hormones are secreted in response to food ingestion – cause insulin to be secreted before glucose absorption
Control of insulin and glucagon secretion Glucagon secretion - stimulated by hypoglycemia, stress - inhibited by glucose, secretin, insulin, and somatostatin Somatostatin secretion - enhanced by almost every factors that increases insulin secretion