Domains and Kingdoms
390 likes | 619 Vues
Sit Where you like Please do not touch microscopes Get a copy of the FIB notes off the front counter. Domains and Kingdoms. 17.3 pages 499-503. Today’s Essential Q uestion : What are the similarities and differences among the 6 kingdoms of life?.

Domains and Kingdoms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sit Where you like Please do not touch microscopesGet a copy of the FIB notes off the front counter
Domains and Kingdoms 17.3 pages 499-503
Today’s Essential Question: What are the similarities and differences among the 6 kingdoms of life?
As we discovered more about the natural world… animal plant not all organisms fit into Linnaeus’s 2 kingdoms (_____ or _____) fungi bacteria Ex: _________ _____ Images from: http://www.leighday.co.uk/upload/public/docImages/6/Listeria%20bacteria.jpg http://danny.oz.au/travel/iceland/p/3571-fungi.jpg
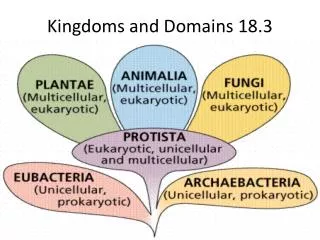
THREE-DOMAIN system Molecular analyses have given rise to a ___________ _______ now recognized = _______ new taxonomic category DOMAIN
Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Domains are larger than Kingdoms and are based on the kind of ____________ an organism has. Ribosomal RNA
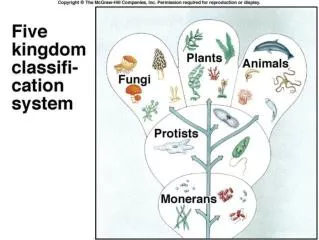
6 Kingdom System Animalia Protista Fungi Plantae Archaebacteria Eubacteria Kidspiration by Riedell
Cell without a nucleus = ____________(Includes bacteria) Cell with a nucleus and organelles surrounded by membranes = _________________ (includes plants and animals) Organism that can make its own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis = ______________ Organism that gets food energy from consuming other organisms = _____________ PROKARYOTE REMEMBER EUKARYOTE AUTOTROPH HETEROTROPH
A ONE-CELLED organism = _____________________ Organism made of many cells = ______________ Polysaccharide made by joining glucose molecules together which makes plants sturdy = _________________ UNICELLULAR REMEMBER MULTICELLULAR CELLULOSE http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/Biol115/Wyatt/default.htm
What are the two broadest categories of the classification system???? Domain Kingdom How many domains are there?
3 Domains • Bacteria • Archea • Eukarya
Domains are based on the characteristics of • Cell Type • Cell Structure • What are the 2 cell types again???
Domains • Archaea and Bacteria are made up of unicellular prokaryotes • Eukarya are made up of multicellular and unicellular organisms that have eukaryotic cells.
The difference between Domain Bacteria and Domain Archaea is the cell structure. • Domain Bacteria - the cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. • Domain Archaea - the cell wall DOES NOT have peptidoglycan
Polymer made of sugars and amino acids found outside the cell membrane in the cell wall in some bacteria = ______________ PEPTIDOGLYCAN http://www.scq.ubc.ca/?p=481
Quick check!! • What are the 3 Domains? • Bacteria are made up of what kind of cells? • Eukarya are made up of what kind of cells? • What's the difference between Domain Bacteria and Domain Archaea?
DOMAIN: BACTERIAKINGDOM: EUBACTERIA PROKARYOTES _______________________ ______________________ Have cell walls with ________________ Can be ____ ____________ or ______________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ UNICELLULAR PEPTIDOGLYCAN AUTOTROPHS HETEROTROPHS E. coli, Streptococcus http://chemiris.chem.binghamton.edu/ZHONG/research/bacteria3.jpg
DOMAIN: ARCHAEAKINGDOM: ARCHAEBACTERIA PROKARYOTES UNICELLULAR _________________ _________________ Have cell walls _________ peptidoglycan Can be___ ___________ or ______________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ LIVE IN EXTREME ENVIRONMENTS like volcanic hot springs, brine pools, low oxygen WITHOUT AUTOTROPHS HETEROTROPHS Halophiles; thermophiles;
http://www.teara.govt.nz/NR/rdonlyres/737B7002-C31D-418D-84C5-D0E68ED87BBB/134228/hero6483.jpghttp://www.teara.govt.nz/NR/rdonlyres/737B7002-C31D-418D-84C5-D0E68ED87BBB/134228/hero6483.jpg THERMOPHILES Organisms that can live in HIGH temperature environments = ________________ Organisms that can live in high salt environments = ______________ HALOPHILES http://web0.greatbasin.net/~wigand/petespaleo/Columbus%20Salt%20Marsh.jpg
What are the kingdoms of Eukarya??? • Protista • Fungi • Plantae • Animalia
DOMAIN: EUKARYAKINGDOM: PLANTAE EUKARYOTES _______________________ ______________________ Have cell walls with ________________ and _____________ _________________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ MULTICELLULAR CELLULOSE CHLOROPLASTS AUTOTROPHS Mosses, ferns, trees, flowering plants http://www.russianflora.com/store/images/product/custom_green_plant_35.jpg
http://www.millan.net DOMAIN: EUKARYAKINGDOM: ANIMALIA EUKARYOTES _______________________ _____________________ ________________ or _______________ __________________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ MULTICELLULAR NO CELL WALLS CHLOROPLASTS HETEROTROPHS Worms, insects, fish, birds, mammals, humans
DOMAIN: EUKARYAKINGDOM: FUNGI EUKARYOTES _______________________ ______________________ Have cell walls with ________________ _______________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ Most MULTICELLULAR; few UNICELLULAR CHITIN HETEROTROPHS- absorb nutrients from decaying organic matter Mushrooms, yeast http://www.ontarionature.org/home/images/mushrooms.jpg
DOMAIN: EUKARYAKINGDOM: PROTISTA EUKARYOTES _______________________ ______________________ Some have cell walls with ________________ ____________________ Can be _____________ or _____________ EXAMPLES: _____________________ Most UNICELLULAR; some colonial/multi CELLULOSE Some have chloroplasts AUTOTROPHS HETEROTROPHS Amoeba; Paramecium; Giant kelp; slime mold http://www.ravelgrane.com/pix/proj/draco/paramecium-nahrung.gif
VirusesAre they alive?? • Viruses are not living so they are not placed in the classification system.