Advanced Electrolyte Processes in Aluminum and Magnesium Extraction
100 likes | 232 Vues
This article explores the intricate details of electrolyte compositions and processes involved in the extraction of aluminum and magnesium through electrolysis. Key components examined include carbon anodes, thermal insulation, and fume collection systems. We discuss the thermal dynamics of alumina and other compounds in the electrolyte, highlighting their roles in reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency. Insights into the dissociation of Al2O3, the role of carbon lining, and the importance of proper current supply and crust management further enhance understanding of this critical industrial process.

Advanced Electrolyte Processes in Aluminum and Magnesium Extraction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
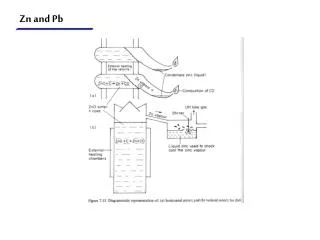
Al & Mg a) Carbon anode; b) Electrolyte; c)Insulation; d) Carbon lining; e) Current collector bar; f) Thermal insulation; g) Steel shell; h) Carbon block; i) Ledge; j) Crust; k) Alumina cover; l) Removable covers; m) Anode rods; n) Fume collection; o) Air cylinder; p) Feeder; q) Current supply; r) Crust breaker
Al …………b.v 1950oC Al2O3………b.t. 2050oC Na3AlF6….. b.t. 1010oC Composition of electrolyte: 5-10% Al2O3 cryolit, AlF3, CaF2,,,LiF – 970 oC 2,1 g/cm3 (Al 2,7 g/cm3 ) Dissociation: Al2O3→ Al 3+ + AlO33- Cathode: Al 3+ + 3 e → Al (l) Anode: 2 AlO33- - 6 e → Al2O3 + 1,5 O2 1,5 O2 + C → 3 CO (CO2) 4F- + C - 4 e → CF4