Analyzing Field Research Methods for Primary Information in Business Management
230 likes | 355 Vues
In the pursuit of understanding market dynamics, organizations often engage in primary research. This paper delves into three significant methods: personal interviews, telephone surveys, and postal surveys, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. Personal interviews foster two-way communication and clarity but can be expensive. Telephone surveys offer quick insights but may lead to consumer hostility. Postal surveys are cost-effective yet suffer from low response rates. This analysis aims to assist businesses in choosing appropriate research methods to enhance decision-making.

Analyzing Field Research Methods for Primary Information in Business Management
E N D
Presentation Transcript
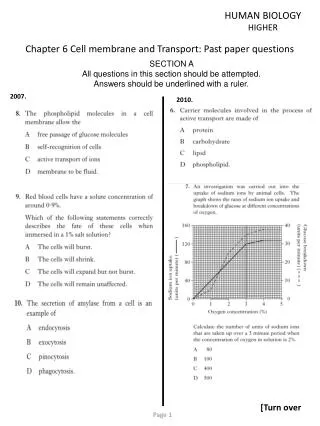
Past Paper Questions Higher and Intermediate 2 Business Management BUSINESS INFORMATION AND ICT
INFO AND ICT – SOURCES OF INFORMATION • HIGHER • 2007Q1a • Organisations continually try to obtain primary information about the market in which they operate. • Describe the advantages and disadvantages of 3 types of field research an organisation could use to obtain primary information. • DISCUSSION – LINKED TO MARKETING UNIT (8)
2007Q1a • Personal interview: • Allows 2-way communication and encourages answers • Misunderstandings can be ironed out • Can be an expensive method • Home interviews tend to be unpopular with consumers • Telephone Survey • Is fairly cheap • Response is immediate allowing large numbers to be surveyed quickly • Hostility to the person making the call is common, people do not like to be disturbed at home
2007Q1a (cont) • Postal Survey • Is cheaper method than street survey as it does not require trained personnel • Questions need to be very simple and easily understood • Response rate is very low • Free gifts are used to increase return rates • High design costs • Wide range of views and opinions • Hall Test • Gives consumers the chance to see or try a product and be questioned on their opinion of the product • Is often used in supermarkets and wholesalers • Fairly cheap method • Can be difficult to analyse qualitative information • Consumers often give favourable replies simply to be polite
2007Q1a (cont) • Consumer Audit • Can be accurate information on consumer buying patterns which can be used to predict consumer trends • Is a very expensive method as many consumers receive payments to complete diaries • Consumers get fed up quickly resulting in a high turnover of respondents and inaccurate data • Consumers may not complete the journals accurately or on time • Test Marketing • Allows for the product to be amended or improved before national launch • Saves the cost of a national launch if the product does not receive good reviews in the test market • Regional tastes may not represent the nation as a whole
2007Q1a (cont) • Observation • Provides accurate quantitative information • There is no direct contact with the customers • Cannot clarify any situations or ask for explanations
INFO AND ICT – TYPES OF INFORMATION • HIGHER • 2004Q4b • Describe 2 suitable types of information required by someone selecting a holiday. Justify your choices. • (4) • INTERMEDIATE 2 • SP Q3a (EQ) • Identify 4 types of information and describe a situation where each would be best used. • (4)
INFO AND ICT– VALUE OF INFORMATION • HIGHER • 2008Q4d • High quality and reliable information is essential if a manager is to make effective decisions. • Describe the characteristics of high quality, reliable information. • (4) • INTERMEDIATE 2 – SOURCES OF INFORMATION • 2008 Q4e (EQ) • Four sources of information are primary, secondary, internal and external. Define each of these sources and give a different example of each. • (8)
INFO AND ICT– VALUE OF INFORMATION • HIGHER • SQP2006Q5a • Discuss the value of secondary information in decision making • (4)
INFO AND ICT – USE OF ICT • HIGHER • 2008Q2d • ICT is used to help Head Office communicate effectively with branches in remote areas of the country. • Explain how modern technology can be used to communicate effectively within an organisation. • (6) • INTERMEDIATE 2 • 2008 Q2c(ii) (EQ) • Identify 2 uses of information in business. (2) • 2007 Q1e (EQ) • Explain 3 ways a business could benefit from using the internet.(3)
Higher 2008 Q2d • • Use of shared resources on LAN’s – work can be done by more than one employee at different branches on the same software or file. • • Staff can have their own area or could have departmental areas where information is stored. • • E-mail – messages can be sent to more than one employee at a time. • • Attachments can be sent between employees. • • Video-conferencing – branch managers can hold meetings without leaving their office, saves costs of travel and accommodation. • • Mobile phones – used by sales person to stay in touch with head office or branches. • • Fax machines – information can be faxed from one branch to another. • • Internet − used to check company website information. • • Powerpoint used for delivering training. • • Spreadsheets – used to show charts/graphs and allow for easier analysis of information. • • Word processing – can be used to send letters, memos, notices to employees. • • Database – can be used to sort large quantities of information for use by staff. (6) • SAME ID BUT DIFFERENT EXPLANATION GAINS MARKS • NO REPETITION OF HOW IT HELPS EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION
Int 2 2008 Q2c • (ii) Identify 2 uses of information in business. • Uses of information in business: • • Plan • • Monitor • • Control • • Make decisions • • Identify new business opportunities.
Int 2 2007 Q1e • (e) Explain 3 ways a business could benefit from using the internet. • • They can sell their goods via the internet. • • They can advertise their goods. • • They can contact suppliers (only one mark should be awarded for communication by e-mail). • • The internet gives them a vast source of information. • • They can use internet for their banking needs. • • They can check information about competitors/new products on the market. • • Widening the market/attracting new market segments. • 1 mark allocated for each relevant point. (3)
INFO AND ICT – USE OF ICT IN BUSINESS • HIGHER • 2005Q1b • Explain how ICT (Information Communications Technology) could support an organisation in the areas of • marketing • human resources • finance (5) • Outline factors which might restrict the use of technology.(4) • INTERMEDIATE 2 • 2007 Q5b (EQ) • Identify 4 forms of ICT (Information Communications Technology) and explain how a large organisation might use each of them. (8)
Higher 2005 q1b • Internet • Organisation can obtain information about potential customers (where, who) • Organisation can obtain information about competitors (prices, products) • Can advertise • Reach a much wider audience • Can sell product on Internet – may save costs of buying/renting premises • Can improve communications by using e-mail/websites • Can improve decision-making due to amount and quality of information available • Interactive CD/DVD • Can provide a means of staff training • CAM/CAD • Can be used to design/produce products – saving labour costs and producing a consistent quality • DTP/Word/Publisher • Used to produce professional looking advertisements, business cards etc • Accounting packages • Used to help with preparation of wages, book-keeping records. • May be used to prepare a cash flow forecast • Databases • Can be used to store staff records • Spreadsheets • Useful for financial record keeping – once set up with formulae calculations can be performed automatically • Reduced wage cost due to increase use of ICT (5)
Higher 2005 Q1b • (ii) Outline factors which might restrict the use of the • technology. • Cost of installation, maintenance and training (one only) • Lack of technical support • Lack of staff knowledge • Reluctance of staff to accept change • Trade union objection if redundancies are likely • Poor signal for mobile phones in certain areas • Compatibility with existing software • Availability of technology e.g. technology for a new invention is • not yet available • (4) • In Part (i) of the question, award a MAXIMUM of 3 marks per functional area • All areas must be addressed to access full marks otherwise apply a MAXIMUM of 4 marks in total
Int 2 2007 q5b • Internet/e-mail • • Send and receive e-mails • • Order supplies from suppliers • • Check on competitors • Video-conferencing • • Have meetings with people in other towns/countries • Database • • Store information on staff, customers, suppliers, etc • • Use mail-merge • Spreadsheet • • Use to calculate staff salaries • • Keep records of payments made to suppliers and all other financial matters • Word Processor • • Use for letters, memos, minutes, reports • Power Point • • Use for presentations, illustrations, etc • Credit all relevant points • Allocate 1 mark for identifying each piece of ICT • Allocate 1 mark for each description (8)
INFO AND ICT – ICT LEGISLATION • HIGHER • 2000Q3b • Describe the legislation, which exists to protect individuals from misuse of information stored about them on computers. • Your answer should include the measures an individual can take to find out what is actually stored about them and what they can do to have incorrect information altered. • (6) • INTERMEDIATE 2
HIGHER 2000 Q3b • Data Protection Act • Organisations must register for the purpose they hold the information • Organisations must not disclose the information in any way that is different from those purposes • Information held must be accurate and up-to-date • Take appropriate steps to keep the information safe • Not hold information any longer than necessary
HIGHER 2000 Q3b CONT… • Individuals can request information held about themselves and have the information corrected or erased • Individuals can complain to the Data Protection Registrar if they feel information held about them is inaccurate or misleading. DPR has the power to have the information corrected. • Claims for compensation can be made against an organisation if an individual suffers damage because of the loss, destruction, unauthorised disclosure or inaccuracy of personal data held.