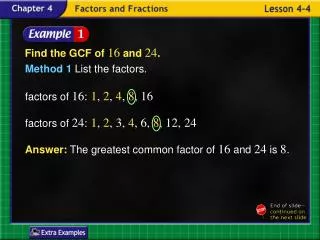
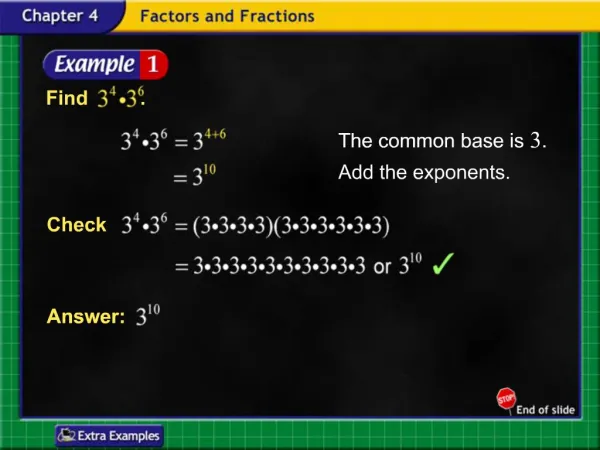
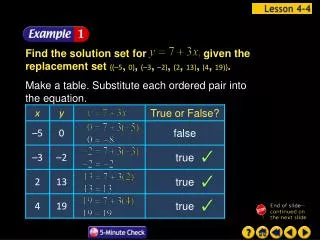
Example 1A:
60 likes | 309 Vues
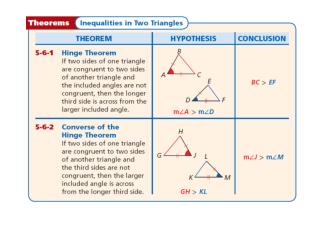
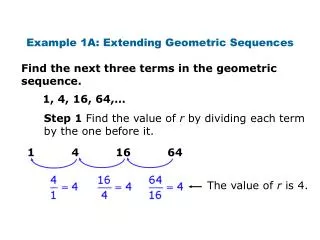
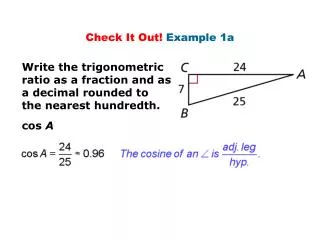
Example 1A:. Compare m BAC and m DAC. Compare the side lengths in ∆ ABC and ∆ ADC. AB = AD AC = AC BC > DC. By the Converse of the Hinge Theorem, m BAC > m DAC. Example 1B:. Compare EF and FG. Compare the sides and angles in ∆ EFH angles in ∆ GFH.

Example 1A:
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Example 1A: Compare mBACand mDAC. Compare the side lengths in ∆ABC and ∆ADC. AB = AD AC = AC BC > DC By the Converse of the Hinge Theorem, mBAC > mDAC. Example 1B: Compare EF and FG. Compare the sides and angles in ∆EFH angles in ∆GFH. mGHF = 180° – 82° = 98° EH = GH FH = FH mEHF > mGHF By the Hinge Theorem, EF < GF.
Example 1C: Find the range of values for k. Step 1 Compare the side lengths in ∆MLN and ∆PLN. LN = LN LM = LP MN > PN By the Converse of the Hinge Theorem, mMLN > mPLN. 5k – 12 < 38 Substitute the given values. k < 10 Step 2 Since PLN is in a triangle, mPLN > 0°. 5k – 12 > 0 Substitute the given values. k > 2.4 Step 3 Combine the two inequalities. The range of values for k is 2.4 < k < 10.
Example 2: Travel Application John and Luke leave school at the same time. John rides his bike 3 blocks west and then 4 blocks north. Luke rides 4 blocks east and then 3 blocks at a bearing of N 10º E. Who is farther from school? Explain. The distances of 3 blocks and 4 blocks are the same in both triangles. The angle formed by John’s route (90º) is smaller than the angle formed by Luke’s route (100º). So Luke is farther from school than John by the Hinge Theorem.
Example 3: Proving Triangle Relationships Write a two-column proof. Given: Prove: AB > CB Proof: 1. Given 2. Reflex. Prop. of 3. Hinge Thm.
Given: C is the midpoint of BD. Example 3B Write a two-column proof. m1 = m2 m3 > m4 Prove: AB > ED 1. Given 1.C is the mdpt. of BD m3 > m4, m1 = m2 2. Def. of Midpoint 3.1 2 3. Def. of s 4. Conv. of Isoc. ∆ Thm. 5.AB > ED 5. Hinge Thm.