Comprehensive Overview of ArcHydro Hydrologic Data Model and Toolset
180 likes | 302 Vues
ArcHydro is a robust data model and toolset developed by David R. Maidment at the University of Texas at Austin, designed to analyze hydrologic systems. It provides a framework for understanding water movement across landscapes using a behavioral model based on the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD). ArcHydro integrates raster and vector data, facilitating the creation of flow networks, hydrologically conditioned DEMs, and catchment delineation. Although it offers semi-automated derivation of key outputs, users must navigate installation challenges and interpret default settings carefully.

Comprehensive Overview of ArcHydro Hydrologic Data Model and Toolset
E N D
Presentation Transcript
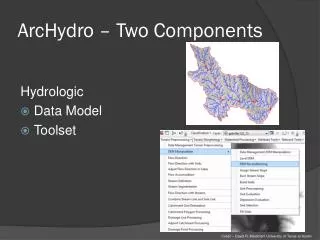
ArcHydro – Two Components Hydrologic • Data Model • Toolset • Credit – David R. Maidment University of Texas at Austin
ArcHydro – Data Model • Based on inventory of all features for an area • Behavioral model – trace direction of water movement across landscape Network Drainage HydroFeatures Hydrography Channel • Credit – David R. Maidment University of Texas at Austin
ArcHydro – Data Model • Developed with National Hydrogrophy Dataset (NHD) in mind • Tools intended to be used with NHD • Integrated raster-vector database • Credit – David R. Maidment University of Texas at Austin
ArcHydro - Tools • Set of tools used to derive end-products • Flow network • Hydrologically conditioned DEM • Iterative, step-by-step approach with required inputs • Raster several formats, vector utilizes geodatabase only
ArcHydro - Tools • Set of tools used to achieve end-products • Flow network • Hydrologically conditioned DEM • Catchment delineation • Iterative, step-by-step approach with required inputs • Raster several formats, vector utilizes geodatabase only • Credit – David R. Maidment University of Texas at Austin
ArcHydro • Cons • Semi-automated • Install can be difficult • User interpretation and editing introduces subjectivity • Need to know what default settings mean • Few training resources • Pros • Semi-automated derivation of key products • Semi-supported • Free • Integrates data from multiple sources and of different types
Hydrologic Modeling • Predict response of hydrologic systems to changing variables, i.e. precipitation • Process-based - try to represent the physical processes observed in the real world • Dozens available – TOPMODEL, SWAT, HSPF, etc. • Variables - Surface runoff, evapotranspiration, etc. • Increasing GIS integration • Credit – Pajaro Valley Water Management Agency
Hydrologic Modeling - Hydraulics • Model hydraulics of water flow over land and through channels • Assess peak discharge, volume estimates, runoff curve numbers, etc. • HEC-RAS • Increasingly GIS-based or integrated
Erosion Analyses • Locate sites of likely gully and other streambank interface erosion • Terrain Analysis approach – Stream Power Index (SPI) • High SPI values indicate high potential overland flow • Quantitative, spatial, repeatable
Water Storage • Utilize LiDAR to accurately identify size, depth, and location of depressions in the landscape • Reduce Peak Flows • Reduce sediment and nutrients transported downstream
Water Storage • NRCS will have tools available in the future to better calculate • Rough calculation • Perform Pit-fill • Subtract original DEM from pit-filled DEM to locate larger depressions • Multiple methods for determining volume
Floodplain Mapping/Delineation • National Flood Insurance Program • Local communities regulatedevelopment in floodplains • Requires accurate floodplain maps • 100 Year Flood boundary • Keep building out of 100 year inundation area
Floodplain Mapping/Delineation • Administered by FEMA • Utilizes Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM) • Update process to digital (DFIRM) • Credit – FEMA
Flood Inundation Area Mapping • Mimic flooding at various stages to determine land area and locations inundated • Needs • Highly accurate land elevation data – LiDARDEM • Modeling Capabilities- Hydraulic Engineering Center–River Analysis System (HEC–RAS) • Stream-gauge heights/peak-flow readings
Flood Inundation Area Mapping LiDAR DEM Stream gauge Data Model (HEC-RAS) Hydrologic Conditioning Calibration Inundation Area Map Conditioned DEM Flood Surface Elevations • Credit – USGS
Flood Inundation Area Mapping Hydrologic Conditioning - Key • Credit – USGS











![G6 - CIRCUIT COMPONENTS [3 exam question - 3 groups]](https://cdn1.slideserve.com/2780393/g6-circuit-components-3-exam-question-3-groups-dt.jpg)






