Early Human Diffusion and The Silk Road
110 likes | 235 Vues
This exploration delves into the origins of modern humans, cultural development, and the pivotal role of the Silk Road in the diffusion of ideas and goods. From the emergence of fully modern humans in East Africa 200,000 years ago to the development of agriculture around 12,000 years ago, movement and cultural evolution were constant. The Silk Road served as a vital link between China, the Mediterranean, and beyond, facilitating trade in silk, spices, and precious metals while promoting cultural globalization. Discover how this ancient network impacted civilizations and continues to resonate today.

Early Human Diffusion and The Silk Road
E N D
Presentation Transcript
For some perspective… • Fully modern humans developed around 200,000 years ago in East Africa • “Culture” (who can tell me what culture is again?)-language, symbols, tools, developed perhaps 50k years ago • Movement had already been happening! Even human ancestors had left Africa
From there: • Culture developed and evolved in many places—some totally cut off from elsewhere and some not • Agriculture developed around 12,000 years ago in the Middle East • Most people did not come into contact with goods or people from more than a few miles from their birthplace
However, • Ideas filtered between civilizations and spread • What’s this called again?
What’s a luxury good for an NDP freshman? What’s something really valuable to you? • Why?
Imagine you’re in the Mediterranean region in the 2ndcentury… • Valuable goods? Silk, precious metals, spices • And thus…
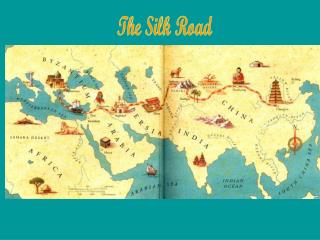
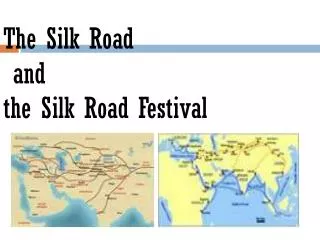
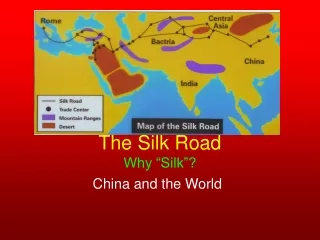
The Silk Road! Start: then-China capital, Chang-An End: Mediterranean ports, India
Silk Road • Series of routes across Asia that carried goods and ideas between Chinaand Europe through central Asia, India, and the Middle East • How would the Silk Road promote cultural diffusion? • Was the Silk Road globalization?