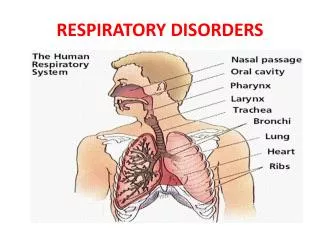
Lower Respiratory Disorders
1.01k likes | 1.87k Vues
Lower Respiratory Disorders. Continued Pulmonary edema - Aspiration. Pulmonary edema. Rapid shift of fluid from the plasma to pulmonary interstitial tissue and alveoli Causes impaired gas exchange. Pulmonary edema. d/t left ventricular failure Backed up blood in the pulmonary vein

Lower Respiratory Disorders
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lower Respiratory Disorders Continued Pulmonary edema - Aspiration
Pulmonary edema • Rapid shift of fluid from the plasma to pulmonary interstitial tissue and alveoli • Causes impaired gas exchange
Pulmonary edema • d/t • left ventricular failure • Backed up blood in the pulmonary vein • h pressure in pulmonary vascular system • Fluids “leak” into interstitial space & alveoli
Pulmonary edema Etiology / Contributing factors • Left ventricular failure • Fluid overload • IV’s • Drug OD
Pulmonary edema Clinical Manifestations • Dyspnea • Sudden • Orthopnea • Cyanotic (central) • “air hunger” • Tachypnea • Cough • Copious sputum • Frothy • Blood tinged
Pulmonary edema Clinical Manifestations • Pulse • Tachycardia • Bounding • BS • Crackles • Fine course • Engorged neck & hand veins
Pulmonary edema Clinical Manifestations • Anxiety • Confusion • Stupor
Pulmonary edema Diagnostic exam • Auscultation • Crackles • X-ray • V/S • Tachycardia • Tachypnea • Pulse oximetry • i • ABG’s • PaO2 • i
Pulmonary edema Treatment • Goal: • Remove fluid • h oxygenation • O2 • Mask • Non-rebreather • Mech. Vent • PEEP
Pulmonary edema • Diuretics • Lasix • Digitalis / Digoxin lanoxin Bronchodilators • Aminophylline • Morphine • i peripheral resistance • i pressure in pulmonary capillaries • i leakage • i anxiety
Pulmonary edema • Which of the following electrolytes must be closely monitored in a patient on Lasix diuretic therapy? • Chloride • Hydrogen • Magnesium • Potassium • Sodium
Pulmonary edema • What nursing actions must be performed before administering digitalis? • This is not multiple choice – you should know this one cold! • What do you do if the apical pulse is <60?
Pulmonary edema Diagnosis: • Impaired Gas Exchange: the fluid –filled alveoli decreases the exchange of gases Out come: • the client will demonstrate improved gas exchange, as evidenced by rising PO2 to 55 or 60 mm Hg, Oxygen saturation above 90%, normaralizing pH, decreasing anxiety and dyspnea, and fewer crackles
Pulmonary edema Nursing management • Diet • Sodium • Low • Potassium • High • Fluids • Decreased / restricted • I&O • Weights • Q day
Pulmonary edema Nursing management • Position to promote circulation • HOB h • Dangle legs
Pulmonary edema Nursing management • Provide psychological support • Monitor meds
Acute Respiratory Failure Definition • Sudden & life-threatening • i gas exchange “It exists when the exchange of O2 for CO2 in the lungs cannot keep us with the rate of O2 consumption & CO2 production.” • Ventilation & Perfusion are impaired
Acute Respiratory Failure ABG’s • PaO2 • < 50 mmHg • PaCO2 • > 50 mmHg • Arterial pH • < 7.35
Acute Respiratory Failure Causes of ARF • i respiratory drive • TBI, MS, Sedatives, hypothyroidism • Dysfunction of the chest wall • Nerve, spinal cord, neuromuscular junction disorders • Dysfunctional Lung Parenchyma
Acute Respiratory Failure S&S • Early • Restlessness • Fatigue • H/A • Dyspnea • Respirations • Air hunger • Pulse • h • BP • h
Acute Respiratory Failure S&S • Progresses • Confusion • Central cyanosis • Diaphoresis • Resp. arrest
Acute Respiratory Failure Nursing management • Assist with intubation & maintain mechanical ventilation • Assess respiratory status • LOC • ABG’s • SpO2 • VS
Acute Respiratory Failure Nursing management • Implement strategies to prevent complications • TCDB • Oral care • Skin care • ROM • Address problems that led to ARF
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • AKA • ARDS • Adult Respiratory distress syndrome
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • ARDS is acute, • Severe injury to most or all of both lungs. • ARDS is not a specific disease; • ARDS can be confused with congestive heart failure • IT is respiratory failure that occurs as a result of massive trauma to the lungs
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Characterized by • sudden and progressive pulmonary edema • increasing bilateral infiltrates on chest x-ray • Hypoxemia • reduced lung compliance • Not due to left side heart failure • Occurs as a result of injury to alveolar capillary membrane • (D/T: aspiration, drug OD, smoke, infection, shock, trauma, sepsis*)
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Injury • Inflammatory response • release chemical (histamine etc.) which cause injury to the alveolar capillary membrane • Leakage of fluid into the alveolar interstitial space and alt. Capillary beds • Protein, blood cells and fluid enter alveoli
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Decrease in surfactant • Alveoli collapse (atelectasis) and fibrotic changes • Lungs become stiff, less compliant, very hard to inspire • Decrease in gas exchange /shunted • Hypoxia • Atelectasis and edema worsen • Lungs may hemorrhage
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Etiology/Contributing factors • Infection • Trauma • Narcotic OD, • Inhalation of irritants • Aspiration
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Clinical manifestations • Rapid onset of severe dyspnea • with in 12-48 hours • Intercostal and suprasternal retractions • Increased resp rate • Crackles • Hypoxemia that does not respond to O2 • Confusion anxiety • Restlessness, apprehension • Cyanosis
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • ABG’s • PaO2 • < 70mmHg • PaCO2 • > 35 • HCO3 • Normal • < 22 • pH • low • Analysis • Resp. and met. Acidosis
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Diagnostic exams/procedures • X-ray • appears to be white due to excessive fluid in the lungs
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Treatment • O2 Intubation and mechanical vent. • Maintain PaO2 at > 60mm Hg • PEEP • Improves oxygenation • Increases functional residual capacity • Reverse alveolar collapse • Use a lower FiO2 • Systemic hypotension • Fluid leakage
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Pulmonary vasodilators • Surfactant replacement • Corticosteroids • Sedatives • due to anxiety and ventilator • Diuretics • Circulatory support • Adequate fluid volume • May limit fluids • Nutritional • Neuromuscular blockers / paralytic drugs
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome • Nursing intervention • Rest • Change position • monitor O2 sat in different positions • High fowlers • Prone • Complications • High death rate (50-60%) • No one recovers 100%
Pulmonary Hypertension • Pathophysiology • Pulmonary arteries narrow • Vasoconstriction • Increased Pulmonary BP • (>30 mmHg) • How do you measure pulmonary BP? • Only can be measured during right side heart catheterization
Pulmonary Hypertension • Pathophysiology • If increase in BP • Right ventricle has to work harder • Right ventricle hypertrophy • enlargement and dilation • Right ventricle fails • Precursor to Cor Pulmonale
Pulmonary Hypertension • Etiology/Contributing factors • Primary: • Rare • Female > Male • Age 20-40 years • hereditary tendency • usually die within 5 years of diagnosis • Secondary: • Existing cardiac or pulmonary disease • Mitral valve disease • COPD
Pulmonary Hypertension • Clinical manifestations of • Pulmonary hypertension without right sided heart failure • (Not clinically evident until late in progression) • Dyspnea and fatigue that worsens over time • Cyanosis and Tachypnea • Crackles and decrease breath sounds
Pulmonary Hypertension • Clinical manifestations of… • Right sided heart failure • Peripheral edema • Ascites • Distended neck veins • Liver engorgement • Crackles • Heart murmur
Pulmonary Hypertension • Diagnostic exams/procedures • ABG’s: • PaO2 • Decreased • Hypoxemia • PaCO2 • Increased • Hypercapnia
Pulmonary Hypertension • Diagnostic exams • ECG • Shows right ventricular hypertrophy • Cardiac catheterization • Right sided heart catheterization only way to measure pulmonary pressure • X-ray • Pulmonary function test
Pulmonary Hypertension • Treatment • Oxygen therapy • Vasodilators (in some people) • Anticoagulants – • Warfarin (Coumadin) • Diuretic to decrease blood volume • Heart/lung transplant • Really there is no cure – death within 2-3 years of diagnosis unless transplant
Pulmonary Hypertension • A 66-year-old client takes a potassium-depleting diuretic. Foods that will help to keep the client’s potassium level within normal limits include • Bananas • Oranges • Cantaloupe • fish • Spinach • whole-grain cereals
Pulmonary Heart Disease • Pathophysiology • Right ventricular failure d/t increased pulmonary pressure • Pulmonary artery vasoconstriction • Right ventricle has to work harder • Right ventricle fails
Pulmonary Heart Disease • Right ventricle does not empty normally • Backward buildup • Increase in Right atrial and systemic venous blood volume • Jugular neck veins distend • Peripheral edema • Angina from right ventricle ischemia
Pulmonary Heart Disease • Clinical Manifestations (right vent. failure) • Edema • Feet • Legs • Distended neck veins • Enlarged palpable liver • Pleural effusion • Ascites • Heart murmur
Pulmonary Heart Disease • Medical treatment • Improve ventilation • Treat lung disease • Treat heart disease • Lung disease • O2 • Chest physiotherapy • Bronchial hygiene • Intubation • Heart disease • Bed rest • Na restriction • Diuretic • Digitalis
Pulmonary Heart Disease • Nursing management • Monitor ventilators • Monitor heart and lungs • O2 • Na Restriction diet • Diuretics • Stop smoking
Pulmonary Emboli Pathophysiology • Emboli: • foreign object that travels through the blood stream • blood clot • Air • Fat • Thrombus (thrombi – pl) • A stationary clot