Solubility
120 likes | 465 Vues
Solubility. November 2012 INB 62. Mixtures Review. 2 or more substances physically combined Can be different throughout (heterogeneous) Granite (2+ Solids) Orange Juice with Pulp (Solid and liquid) Oil and Vinegar (2 Liquids) Can be the same throughout (homogeneous)

Solubility
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Solubility November 2012INB 62
Mixtures Review • 2 or more substances physically combined • Can be different throughout (heterogeneous) • Granite (2+ Solids) • Orange Juice with Pulp (Solid and liquid) • Oil and Vinegar (2 Liquids) • Can be the same throughout (homogeneous) • Salt Water (Solid and Liquid) • Stainless Steel (Iron, Chromium, Nickel) (2+ Solids) • Milk • Air without Clouds (2+ gases)
Separating Mixtures • Melting/Boiling Points • Magnetism • Density (Float / Sink) • Centrifuging • Distillation • Filtering • Chromatography
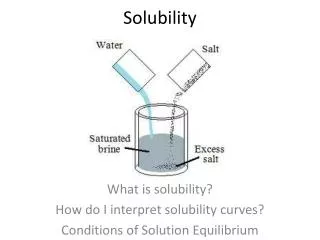
Solubility • The property of a substance to dissolve into another substance • Soluble: Capable of dissolving • Insoluble: incapable of dissolving
Solute • The substance that gets dissolved • The substance with the SMALLER amount
Solvent • The substance that the SOLUTE gets dissolved into • The substance with the GREATER amount
Solution • A homogeneous mixture of one or more solutes dissolved into a solvent
Examples! • Solutes: Sugar, Color, Flavor Solvent: WaterSolution: Kool-Aid • Solutes: Silver, CopperSolvent: GoldSolution: 14 karat Gold • Solute: SaltSolvent: WaterSolution: Oceans • Solutes: Carbon Dioxide, Sugar, FlavorSolvent: WaterSolution: Soda
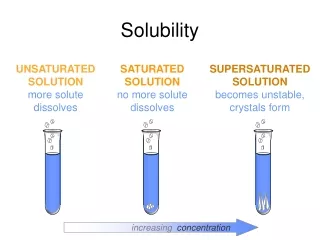
More Vocabulary! • Unsaturated • The solvent can hold more solute • Saturated • The solvent is holding as much solute as it can • Supersaturated • The solvent is holding more solute than it can
Factors Affecting Solubility • Nature of Solute and Solvents • Temperature of the solvent • Amount / speed of “stirring” • Surface Area of the solute • Pressure
Review Solutions • Can you see two parts in solutions or are they mixed together so well you only see one thing? • you only see one thing • Are solutions mixtures or pure substances? • Mixtures • What kind of states can a solution be? • Solid, liquid, or gas • What are the two “s” words that every solution must have? • A solute and a solvent
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas) Mixtures Can see two parts Pure Substances You can only see one thing because there is only one kind of particle in it. (Examples?) Mechanical Mixture Can see two parts.(Examples?) Solutions They’re mixed together so well you only see one thing – it looks pure but it isn’t Solventis the one doing the dissolving.(Examples) Solute is the substance to be dissolved.(Examples?) INB 61