Understanding Cell Division: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Explained
270 likes | 427 Vues
Explore the fascinating process of cell division, crucial for growth and reproduction in both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Discover the stages of the cell cycle, including G1, S, G2, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Learn how cells prepare to divide by synthesizing proteins and duplicating DNA. Witness the precise division of the nucleus during mitosis and the formation of new cells through cytokinesis. Understand the importance of maintaining a chemical balance across the cell membrane and how this influences cell size and division.

Understanding Cell Division: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
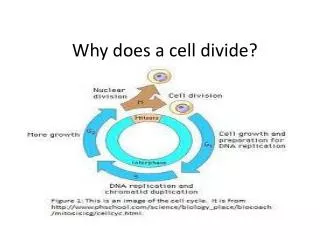
G1 phase: Growth, cytokinesis finishes , protein synthesis, prepares to copy DNA • S phase: DNA copies itself • G2: protein synthesis continues prepares to divide • M Mitosis Nucleus divides perfectly • Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides sort of evenly
Unicellular organisms • Mitosis is reproduction • Nutrients, oxygen come in across the cell membrane. Waste products leave through the cell membrane. • The ability to maintain a chemical balance across the cell membrane is vital. • As the cell grows the volume increases faster than the surface area of the membrane. • When the cell can no longer maintain the traffic across the membrane. It signals the cell to divide.
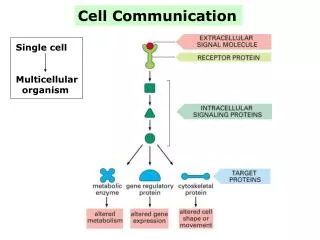
Multicellular Organisms • If cells are limited to their size then in order to have large organisms they become multicellular. • Cells specialize into tissues each with a certain job. Nerves for communication and sensing, muscles for moving, digestive system for attaining food etc. • Each of these cells contain all the DNA but to specialize they turn off certain genes and turn on others.
How do cells divide?Mitosis and cytokinesis • Mitosis • How the nucleus divides exactly • Uncoiled DNA copies itself (Chromatin threads) • DNA coils up (Chromosomes) • Centrioles go to each end of the cell • Micro tubules attach to chromosomes • Microtubules pull them apart • Mitosis - YouTube
Phases of mitosis • Prophase coil up • Metaphase line up • Anaphase separate • Telophase uncoil
Cytokinesis • Cytoplasm divides • At the end of telophase
Intephase Onion root tip White fish ovaries
Prophase cell prepares to divide Early prophase Late Prophase
Prophase • DNA coils up into Chromosomes • Centrioles migrate to the 2 poles • Aster starts to form • Nuclear envelopes disintegrates • Chromosome are doubled in chromatid pairs.
Prophase In allium root tip In white fish ovaries
Metaphase • Centrioles form a complete spindle • Microtubules attach to the kinetichores of the chromatid pairs • Chromatid Pairs line up across the equator . • Nuclear membrane is gone
Metaphase In allium root tip In white fish
Anaphase • The micro tubules shorten and pull the chromatids apart. • The chromatids migrate to opposite ends of the cell • The micro tubules push the cell membrane make the cell longer
Anaphase In allium root tips In white fish ovaries
Telophasetwo new nuclei reform Early telophase Late telophase
Telophase • This is prophase backwards • The nuclear envelope reforms. • The chromosomes uncoil • The aster disappears • The cytoplasm starts to divide
Telophase In allium root tips In white fish ovaries
Cytokinesis Allium root tip White fish ovaries